Magnets show up in everyday life more than most people realize. They’re the “behind-the-scenes” reason your fridge stays sealed, your headphones make sound, and motors spin inside everything from fans to washing machines.
In short: the most common uses of magnets are to hold and latch parts, convert electricity into motion, turn signals into sound, store data, and separate metals. Below are 10 real, easy-to-spot examples—plus a quick explanation of what the magnet is actually doing in each one.
10 Uses of Magnets in Daily Life (Real Examples)
As already mentioned above, magnets are used for a number of purposes some of which we are going to discuss now.
| # | Device / Example | Magnet type | What it does (5–8 words) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Refrigerator door gasket | Permanent magnet strip | Keeps door sealed, stops cold leaks |
| 2 | Speakers & headphones | Permanent magnet + voice coil | Moves diaphragm to create sound |
| 3 | Dynamic microphone | Magnet + moving coil | Turns sound vibration into signal |
| 4 | Appliance electric motors | Permanent magnets / electromagnets | Converts electricity into spinning motion |
| 5 | Computer hard drive (HDD) | Magnetic recording + actuator magnets | Writes/reads data on spinning platters |
| 6 | MRI machine | Superconducting electromagnet | Creates strong field for body imaging |
| 7 | Recycling crane / scrapyard | Electromagnet | Lifts steel, drops it on command |
| 8 | Food processing separator | Permanent magnet / magnetic grate | Catches metal bits before packaging |
| 9 | EV motor & ABS wheel sensor | Permanent magnets + magnetic sensors | Drives motion, measures wheel speed |
| 10 | Classroom whiteboard & experiments | Permanent magnets | Holds items, demonstrates fields/poles |
1. Refrigerator Door Seals 🧊
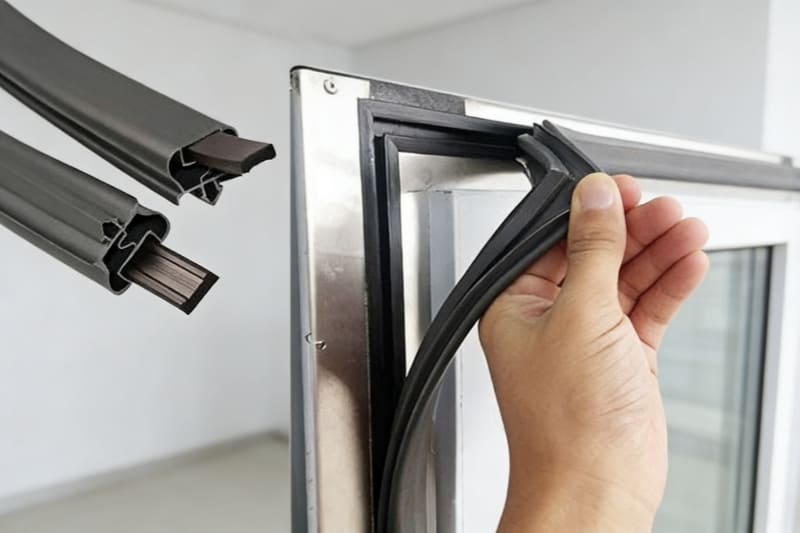

What it is: Magnets help refrigerator doors stay tightly closed.
Real example: A magnetic strip inside the door gasket pulls the door against the metal frame to keep the seal airtight.
What the magnet does: Magnets are used in refrigerators to keep the door tightly closed. Inside the refrigerator door gasket, there is a thin magnetic strip that pulls the door toward the metal frame. This helps maintain an airtight seal, prevents cold air from escaping, and supports better energy efficiency.
2. Speakers & Headphones 🎧

What it is: Magnets are used to produce sound in audio devices.
Real example: Earbuds and speakers contain a magnet and voice coil that move a diaphragm to create sound waves.
What the magnet does: Speakers and headphones rely on magnets to produce sound. In these devices, a magnet works together with a voice coil to create motion. When an electrical signal passes through the coil, it interacts with the magnetic field and moves a diaphragm back and forth, which produces sound waves that we can hear.
3. Microphones (Dynamic Mics) 🎤
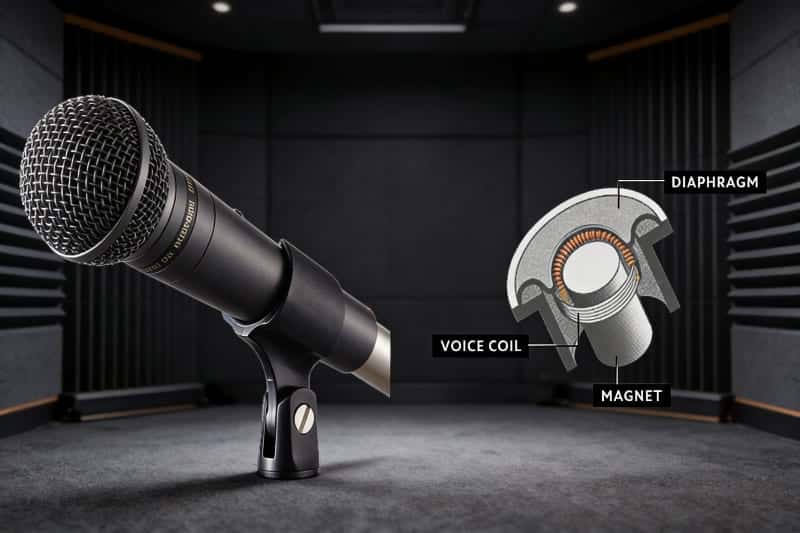

What it is: Some microphones use magnets to convert sound into an electrical signal.
Real example: In a dynamic microphone, sound vibrations move a diaphragm connected to a coil placed near a magnet.
What the magnet does: Microphones can work in a reverse way compared to speakers, and magnets play an important role in this process. In a dynamic microphone, sound vibrations move a diaphragm connected to a coil placed near a magnet. As the coil moves within the magnetic field, it generates an electrical signal, which is then processed and recorded as sound.
4. Electric Motors in Home Appliances 🌀
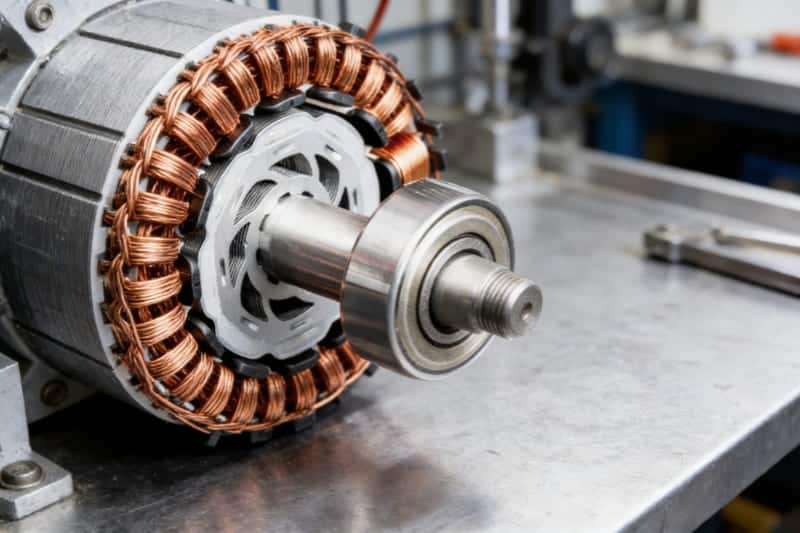
What it is: Magnets help electric motors create motion in household machines.
Real example: Fans, washing machines, blenders, and vacuum cleaners rely on motor-driven rotation.
What the magnet does: Many home appliances depend on electric motors, and magnets are essential for those motors to function. Devices such as fans, washing machines, blenders, and vacuum cleaners use magnetic fields to create rotation. In this way, magnets help convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, allowing machines to spin, mix, or pump as needed.
5. Computer Hard Drives (HDD Data Storage) 💾

What it is: Magnets are used to store and read data in traditional hard drives.
Real example: HDDs store information on spinning platters, where tiny magnetic areas represent digital data.
What the magnet does: Magnets are also used in computer data storage, especially in traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). The hard drive stores information by changing the magnetic orientation of tiny areas on a spinning disk. The drive then reads the direction and pattern of these magnetic segments to retrieve the stored data. Thus, magnetism becomes a key method for writing and reading information.
6. MRI Machines (Healthcare Imaging) 🏥
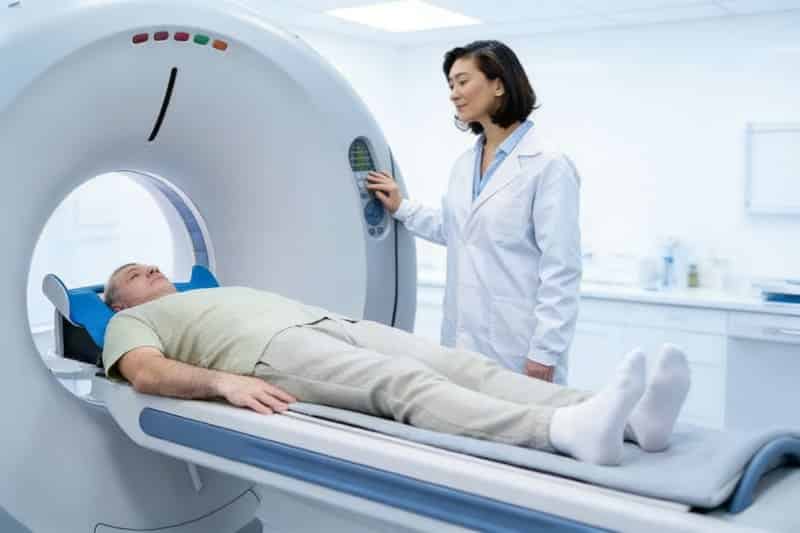
What it is: MRI scanners use strong magnets to create medical images.
Real example: Hospitals use MRI machines to view soft tissues like the brain, joints, and organs in detail.
What the magnet does: In the medical field, magnets are widely used in MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines. MRI equipment contains very strong magnets that help generate detailed images of the inside of the human body. This makes it possible for doctors to examine organs, joints, and soft tissues with high accuracy and without invasive procedures.
7. Recycling & Metal Sorting ♻️
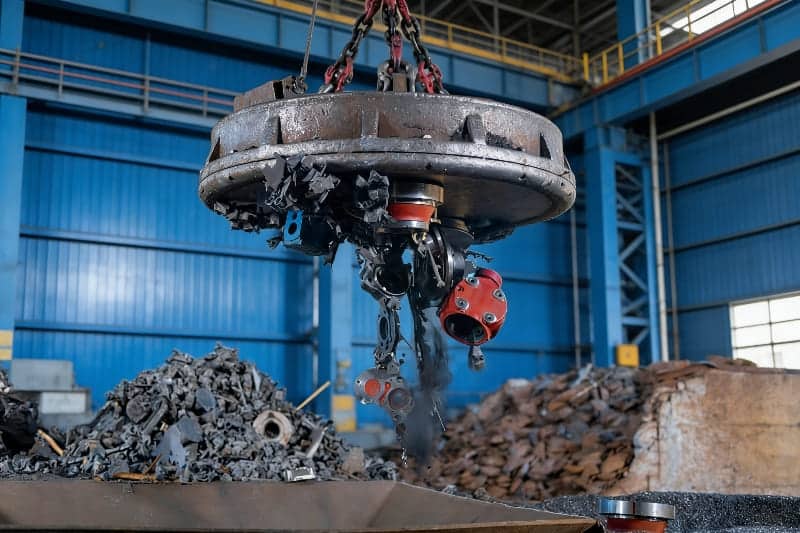

What it is: Magnets are used to separate and move ferrous metals in recycling.
Real example: Scrapyards use crane-mounted electromagnets to lift steel and iron from mixed scrap piles.
What the magnet does: Magnets are extremely useful in recycling plants and scrapyards where metal needs to be separated efficiently. Electromagnets can lift and move large quantities of iron and steel, separating them from non-magnetic materials. Because the magnetic force can be switched on and off, this process becomes fast, controlled, and practical for heavy industrial work.
8. Food Processing Separation (Metal Contaminant Removal) 🌾
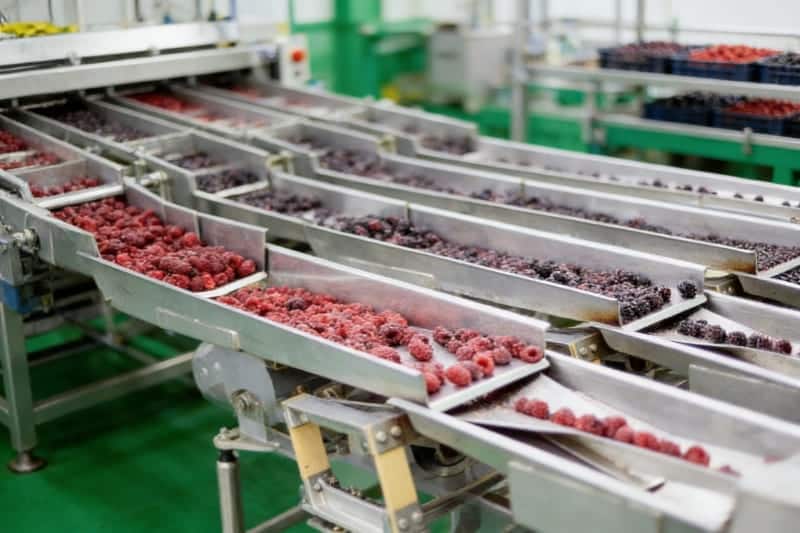

What it is: Magnets help remove metal contaminants during food production.
Real example: Grain and flour processing lines use magnetic separators to catch metal shavings before packaging.
What the magnet does: In food processing units, magnets are often used to remove small metal contaminants from products such as grains, flour, and other food materials. During production and transportation, tiny metal pieces can sometimes enter the processing line. Magnetic separators help catch these particles before packaging, improving safety and protecting machines from damage.
9. Transportation & Automotive Systems 🚗

What it is: Magnets support vehicle motion and sensing systems.
Real example: EV motors use permanent magnets to generate strong torque and efficient motion, and ABS systems rely on magnetic sensors to monitor wheel speed.
What the magnet does: Magnets play an important role in transportation, especially in modern vehicles. Electric vehicle motors commonly use permanent magnets to generate strong torque and efficient motion. In addition, automotive systems such as ABS (Anti-lock Braking Systems) rely on magnetic sensors to monitor wheel speed. This helps prevent wheel lock-up and improves safety during sudden braking.
10. School Use (Classroom & Learning) 🏫
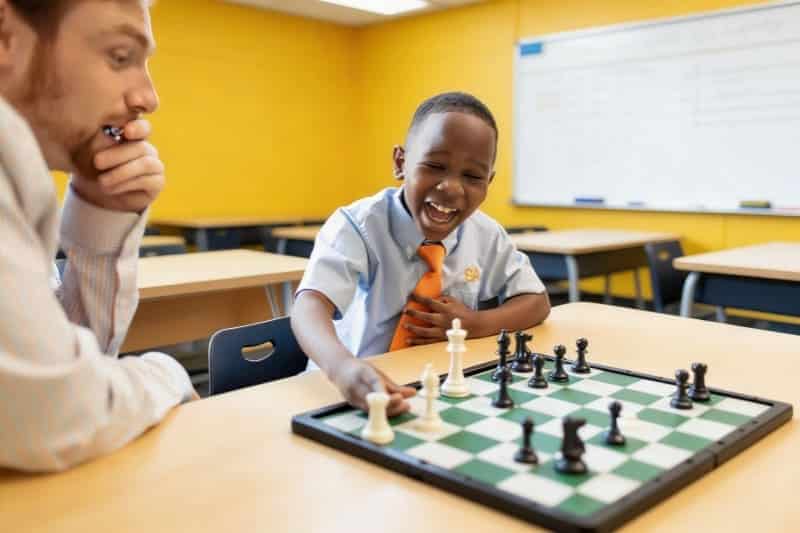

What it is: Magnets support teaching, experiments, and classroom organization.
Real example: Teachers use magnets to hold materials on whiteboards, and students use simple magnets and compasses to explore attraction, repulsion, and magnetic fields.
What the magnet does: Magnets are not only used in industries, but also in schools for learning and classroom organization. Teachers often use magnets to hold papers, charts, and learning materials on whiteboards. In science lessons, magnets help students understand basic concepts such as attraction and repulsion, poles, and magnetic fields through simple experiments that are easy to observe and remember.
Safety Notes (Especially for Strong Magnets)
Magnets are useful, but strong magnets can also cause damage or injury if used carelessly.
- Don’t let strong magnets snap together. Neodymium magnets can pinch skin or even chip/crack on impact.
- Keep strong magnets away from medical implants. If someone has a pacemaker or other implant, avoid close contact with strong magnets.
- Be careful around HDD storage. Traditional hard drives store data magnetically, so strong magnets can potentially cause issues (SSDs are generally less affected).
- Industrial electromagnets are not toys. Scrapyard cranes and large separators can be extremely powerful and should only be used by trained operators.
Why Magnets Matter in Everyday Life
- They enable efficient energy conversion in motors and generators, turning electrical energy into motion (and vice versa) with less wasted power.
- They power sensing, control, and automation, from simple switches to industrial sensors and systems like ABS that rely on magnetic signals.
- They improve safety and convenience through magnetic locks, door latches, detectors, and other “works-in-the-background” features people depend on every day.
- They make modern electronics more compact and reliable, helping devices deliver strong performance without bulky mechanical parts.
Conclusion
The applications of magnets in everyday life are far more widespread than most people realize. From magnetic notes that stick to refrigerators, to magnetic components that transmit sound in speakers, to magnetic materials that store important data on hard drives, magnets are virtually everywhere. They play a crucial role in household appliances, electronic devices, industrial machinery, medical equipment, and even emerging robotics technology. It is precisely this diversity and practicality that makes magnets an indispensable cornerstone of modern life, with their potential applications continuing to expand.
FAQ
What are the main types of magnets?
Permanent magnets stay magnetized without power, temporary magnets only act magnetic when exposed to a field, and electromagnets create a controllable magnetic field when electricity flows. Electromagnets can be switched on/off and adjusted in strength, which is why they’re widely used in motors, relays, and lifting systems.
Do computers still use magnets?
Yes—many computers still use magnets, especially in hard disk drives (HDDs), cooling fan motors, speakers, and small sensors (like lid/cover detection in some laptops). Modern PCs with SSDs rely less on magnetism for data storage, but magnets still appear in several internal components.
What’s the difference between permanent magnets and electromagnets?
Permanent magnets are always “on” and don’t need electricity, while electromagnets only become magnetic when current flows through a coil. The key advantage of electromagnets is control: you can switch them on/off and change their strength (and polarity) by adjusting the current.
Where do we see electromagnets in daily life?
You’ll see electromagnets in devices that need switchable magnetism, like doorbells, relays, and many electric motors in fans, blenders, and washing machines. They’re also used in higher-power systems such as MRI machines, induction cooktops, and scrapyard cranes because the magnetic force can be precisely controlled.
What are 20 uses of magnets in everyday life?
Magnets are used to create motion (motors), convert energy (generators/transformers), produce sound (speakers/mics), store data (HDDs), sense position or speed (sensors), and hold parts closed (latches). That’s why they show up in everything from kitchen tools to cars and industrial equipment.
20 common uses of magnets in everyday life
- Speakers – turn electrical signals into sound.
- Headphones/earbuds – same principle as speakers, just smaller and more precise.
- Microphones – convert sound vibrations into electrical signals (the reverse process).
- Refrigerator door seals – magnetic strips keep the door closed and airtight.
- Cabinet/door latches – quick, reliable closing without complicated hardware.
- Electric motors in appliances – fans, blenders, washing machines, vacuum cleaners, etc.
- Car components – starter motors, alternators, and many sensors rely on magnets.
- Generators – convert motion to electricity (power plants, portable generators, bike dynamos).
- Transformers – use magnetic fields to step voltage up or down in power systems and chargers.
- Computer hard drives (HDDs) – store information using magnetic recording.
- Magnetic stripe cards – legacy tech on some bank/ID/access cards.
- Compasses – align with Earth’s magnetic field for navigation.
- Magnetic door/window sensors – common in home security systems and alarms.
- Anti-theft tags – retail security tags can be activated/deactivated magnetically.
- Electric bells/relays – electromagnets pull a striker or switch a circuit.
- Induction cooktops – generate heat in cookware through electromagnetic induction.
- Microwaves – the magnetron uses magnets to help generate microwave energy.
- Smartphones & laptops – magnets support speakers, vibration motors, and lid/cover detection.
- Magnetic mounts/holders – phone car mounts, tool holders, knife racks, etc.
- Industrial sorting/lifting – separate ferrous metals in recycling and lift steel safely in factories.
Do computers have magnets in them?
Yes—computers do have magnets inside them, but where they appear depends on the hardware type.
- Hard drives (HDDs): Traditional HDDs rely on magnetism to read and write data on spinning magnetic platters, so magnets are a core part of how they work.
- Speakers/headphone jacks (if built-in): Speakers use a magnet + coil to convert electrical signals into sound.
- Cooling fans: The fan motor uses magnetic fields to spin the blades and move air.
Modern computers that use SSDs (solid-state drives) typically have fewer “data-critical” magnets, because SSDs store data electronically, not magnetically. That said, many laptops still contain magnets for hinge/lid sensors or accessories, and external magnets are generally more dangerous to HDDs than SSDs—strong magnets can interfere with magnetic storage, while SSDs are far less affected.
I also referred to these articles:
use of neodymium magnets in healthcare and their effects on health – PMC

I’m Ben, with over 10 years in the permanent magnet industry. Since 2019, I’ve been with Osenc, specializing in custom NdFeB magnet shapes, magnetic accessories, and assemblies. Leveraging deep magnetic expertise and trusted factory resources, we offer one-stop solutions—from material selection and design to testing and production—streamlining communication, accelerating development, and ensuring quality while reducing costs through flexible resource integration.


