Do Magnets Wear Out over time? Although friction and wear don’t technically “discharge” magnets as they do physical objects, constant variables can cause their magnetic power to dissipate over time.
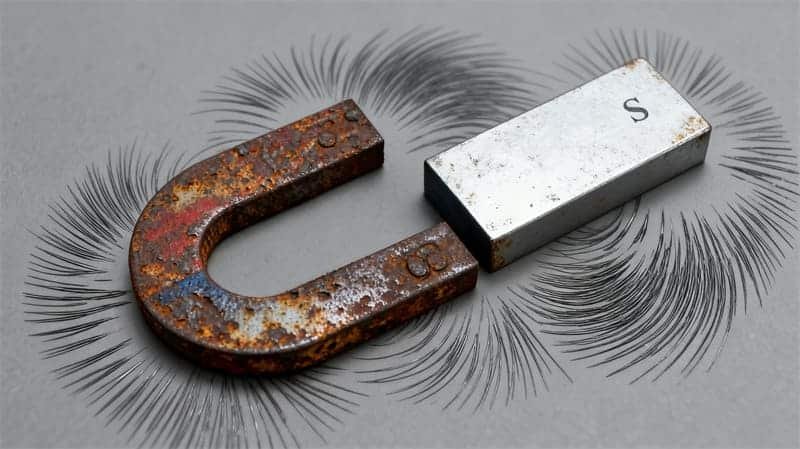

Do Magnets Wear Out Over Time?
In everyday use, you may still wonder: Do Magnets Wear Out in normal household or industrial scenarios?
Yes, but very slowly. Although they do not wear out like batteries or light bulbs, permanent magnets such as ferrite, alnico, samarium-cobalt, and neodymium can slowly lose their magnetic strength in unfavorable environments.
The majority of contemporary permanent magnets retain approximately the same magnetization for decades when properly stored and used.
Thus, exposure to elements such as heat, physical shock, corrosion, or strong opposing magnetic fields can accelerate power loss by misaligning the magnetic domains or causing material damage.
So, even if your refrigerator magnet is unlikely to break during its lifetime, it is still susceptible to environmental factors and the passage of time.
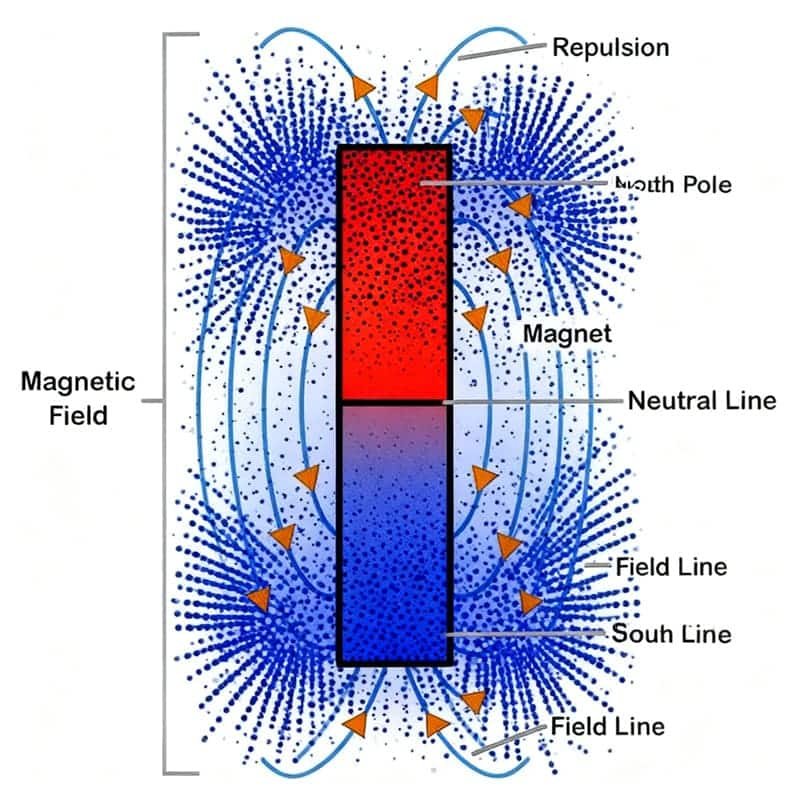
Magnetic Lifespan: How Long Before Magnets Wear Out?
The best way to describe the “lifetime” of a magnet is the amount of time it retains a significant portion of its initial magnetic strength under normal conditions for premium permanent magnets used in suitable environments. Under stable storage, Do Magnets Wear Out measurably within a decade? Typically, losses stay extremely small.
Under ideal conditions, some sources predict a decrease of less than 1% in magnetic strength every 10 years.
Affects a magnet’s lifespan
- Temperature extremes: Heat can completely or partially destroy a substance.
- Physical shocks: When dropped or hit, the magnetic domains become misaligned.
- Anti-magnetic: Polarity can be weakened by prolonged exposure to fields.
- Moisture and corrosion weaken the structure of iron-based magnets.
These factors also answer a common question—Do Magnets Wear Out faster under stress or poor storage?
Extend a magnet’s life
- Extend the life of the magnet:
- Avoid mechanical stress and serious accidents.
- Apply protective coatings to prevent rusting.
- Avoid sources of opposing magnetic fields.
- Use keepers, which are soft iron rods, to maintain domain alignment during storage.
- If properly cared for, a good, hard magnet can last for decades or even centuries.
Important Factors Affecting Magnetic Age:
Temperature: Irreversible domain misalignment causes the magnet to appear above its rated maximum operating temperature. For example, around 80°C, many common neodymium grades begin to degrade permanently.
Corrosion: Damage to protective coatings causes oxidation, which weakens the magnetic material, especially in neodymium magnets, which are fragile and contain iron. (wholesale neodymium magnets)
Non-magnet Strong external magnetic field or opposite direction: Degeneration can be accelerated if the magnet is subjected to 30 alternating fields or sits in a field that opposes its magnetism.
Mechanical damage or physical shock: Sticking or splitting can weaken the magnetic material by reducing its effective strength.
Neo-magnets. In essence, magnets don’t “expire” like milk, but how long they retain their full strength depends on their treatment and environment.
How long do neodymium magnets last?
Common types of rare earth magnets (neodymium, NdFeB) have a fairly long lifespan if properly maintained.
According to the study, a high-quality neodymium magnet can retain most of its magnetic strength for 30 to 50 years under low-stress conditions at normal room temperature. Under ideal conditions, they may actually lose less than 5% of their strength over a century. (Recommended read: How Strong Is a Neodymium Magnet)
Do Magnets Wear Out in Neodymium (NdFeB) Grades?
Yes, but very slowly under the right conditions. Commonly used neodymium, iron, and boron (NdFeB) magnets, among the strongest permanent magnets on the market, retain a high proportion of their initial strength. When properly packaged and used according to specifications. Even then, the practical answer to Do Magnets Wear Out remains “very slowly,” unless abused by heat, shock, or corrosive humidity.
These are some examples of common numbers:
- In one study, NdFeB magnets exposed to the outside for about 12 years showed a flux loss of 1% in 30 years and about 1.3% in 50 years.
- Another explanation is that under most circumstances, you can estimate an age of more than 20 years with less damage. However, under unfavourable conditions (e.g., extreme heat, humidity, or shock), it can be as short as a few years.
- According to a general question, if not overheated, typical neodymium magnets can lose about 1% of their strength in 10 years.
Tips
- Keep outside the upper temperature range recommended by the manufacturer and store in a cool, dry place.
- Protect the cover from being damaged or wet.
- Strong external magnetic fields, including those representing the orientation of magnets
- Prevent fragile magnet material from bending, sticking, or physically impacting.
- By doing this, you can improve the “throw” of your neodymium magnet.
How to make magnets last longer
Magnets are powerful devices used in everything from refrigerators and scientific instruments to speakers and motors. Although permanent magnets can last for years, they can gradually lose their strength due to poor storage and exposure to the elements.
This post describes tried-and-true techniques for protecting and maintaining magnet strength if you’re wondering how to extend their life.
- Proper care and storage of the magnet are essential if it is to remain strong for many years. First, because both can cause problems with internal magnetic alignment, magnets should be kept away from extreme heat and strong opposing magnetic fields.
- Especially for older magnetic types, such as Alnico, placing the magnets with cappers. Soft iron bars attached to the poles can help preserve their magnetic field and prevent demagnetisation.
- Physical protection is also important, as microscopic cracks created by dropping, hitting, or scratching the magnet can disrupt the neat arrangement of the magnetic Si domains within.
- A protective coating can prevent corrosion, a primary factor in long-term deterioration in rare-earth magnets such as neodymium.
- Typically, a magnet can last for decades in a stable environment that is cool and dry and mechanically soft.
What can cause a magnet to lose its magnetic properties?
When the internal domain alignment is disrupted, magnets lose their magnetic properties. They have several reasons.
Volume loss
A magnet’s magnetic field decreases when it physically loses material due to wear, corrosion, or abrasion. Because less magnetic material is available to generate a force.
Neodymium magnets exposed to moisture and lacking protective coatings are particularly susceptible to this. Lower magnetic strength is a direct result of reduced volume.
External demagnetizing fields
A magnet can also weaken when exposed to strong external magnetic fields. For example, two magnets with opposite poles can partially demagnetise each other over time. (Recommended reading: How Strong Is a Neodymium Magnet)
Magnetic fields generated by electric current in adjacent devices can cause a disturbance in the magnet’s domain, which gradually reduces its strength.
Heat
One of the most important variables affecting the performance of a magnet is temperature. The internal structure of the magnet changes, and it permanently loses its ability to attract electricity when heated above a certain threshold, sometimes called the Curie temperature in weak materials.
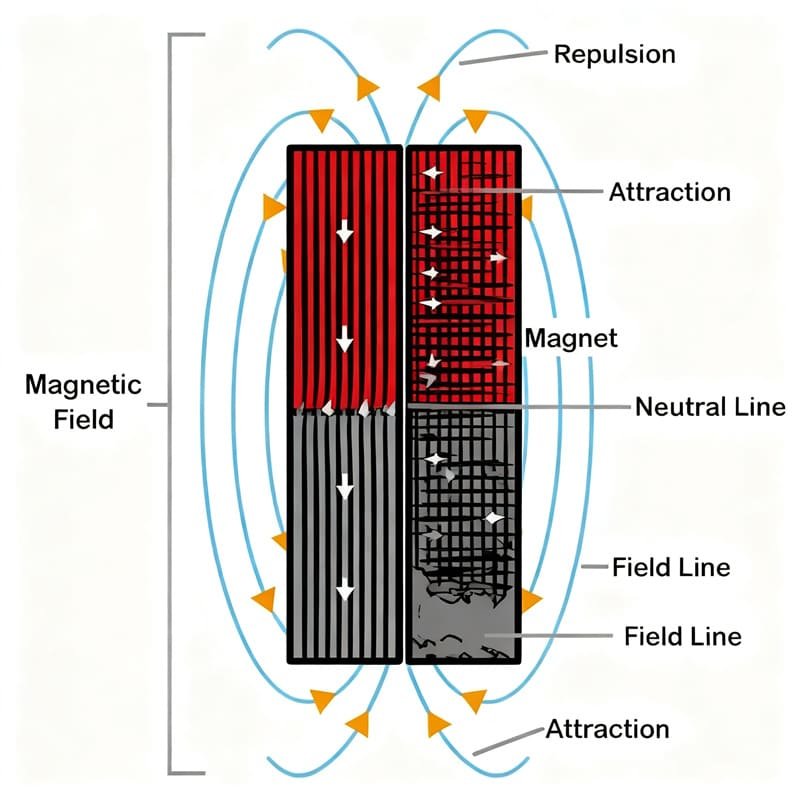
Magnetic stability
The material and structure of a magnet determine how stable its magnetic field is. Neodymium, samarium (NdFeB), cobalt (SmCo), and Alnico magnets are examples of permanent magnets that last for many years, sometimes decades.
But even the strongest magnets can lose their strength over time. The internal magnetic domains of a magnet are small sections that point in the same direction. This has been done incorrectly over time, which causes this damage.
This alignment can be disrupted by things like extreme heat, physical trauma, or exposure to opposing magnetic fields, which reduces the magnet’s total strength.
An important factor in magnetic stability is temperature. Every magnet has a Curie temperature, which is the point at which it completely loses its ability to attract.
Samarium-cobalt magnets can withstand temperatures above 300°C (572°F), but neodymium magnets lose their ability to magnetise at 80°C (176°F). A magnet can become permanently demagnetised if it is operated near or above its Curie temperature.
Magnet storage and considerations
The long-term strength of a magnet depends on proper storage. Magnetic fields can be weakened by demagnetisation or by attracting metal debris when they are stored carelessly.
Important elements of magnetic storage
- Humidity
- Temperature
- Physical effect
- Corrosion interference with magnetic fields
Things to consider when using magnets
- The safety of the individual: Strong magnets can pinch a finger. Wear gloves when working with large magnets.
- Office and Home Safety: Children and dogs should not be near magnets. Avoid placing magnets near electronic storage devices.
How to prevent demagnetization
- Prevent high temperatures:
Magnets should not be near heat sources, as this can cause their domains to reattach and reduce their magnetic strength.
- Reduce mechanical shock:
Micro-fracture or misalignment caused by dropping or bumping of the magnet may result.
- Store with keepers:
Place soft iron keepers on the poles of the bar magnets. By doing this, field loss is avoided, and its magnetic circuit is protected.
- Stay away from hostile fields:
Magnets should not be near strong electromagnetic fields that could reverse their polarity.
- Dry environment:
Store magnets in a dry place to prevent them from rusting, especially neodymium magnets that are prone to rust.
Conclusion
Although magnets can weaken over time, it usually happens very slowly, over decades under normal conditions. Magnets can be kept strong and active for many years with proper handling, temperature management, and storage. Knowing how to preserve
Magnetic stability, in addition to extending the life of magnets, guarantees their reliability in critical applications, such as household appliances and research instruments.
By protecting the magnet from heat, collisions, and opposing fields, its magnetic strength can be preserved for decades. Magnetization can also help a disabled person recover.
Simply put, magnets “wear out,” yet with proper care, they can remain magnetized for nearly a lifetime.
FAQ
Can magnets be remagnetized?
In many situations, it is possible to remagnetize the magnets. During the procedure, a powerful external magnetic field oriented in the desired direction is applied to the magnet.
For example:
Special coils or electromagnets are used in industrial demagnetization to increase or restore magnet strength.
Although the effect is usually mild, small-scale techniques such as rubbing a strong magnet against a weak one can sometimes increase its magnetisation.
So, complete demagnetization may not be possible if the internal structure of the magnet is damaged (e.g., by heat or fracture).
Refer: neodymium magnets wiki

I’m Ben, with over 10 years in the permanent magnet industry. Since 2019, I’ve been with Osenc, specializing in custom NdFeB magnet shapes, magnetic accessories, and assemblies. Leveraging deep magnetic expertise and trusted factory resources, we offer one-stop solutions—from material selection and design to testing and production—streamlining communication, accelerating development, and ensuring quality while reducing costs through flexible resource integration.

