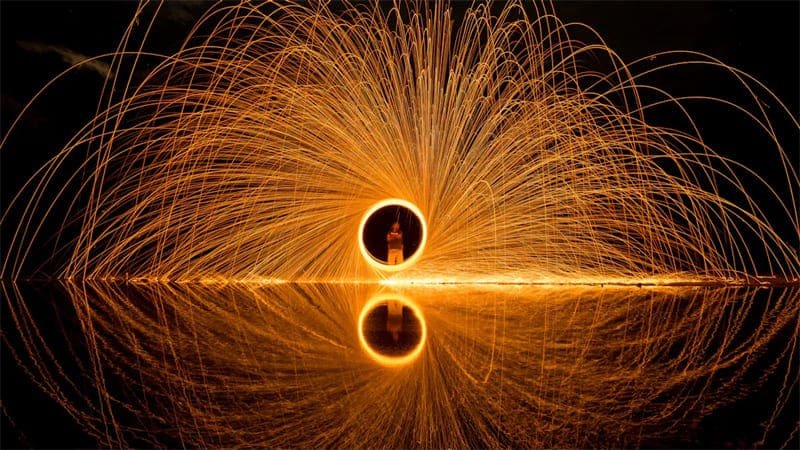
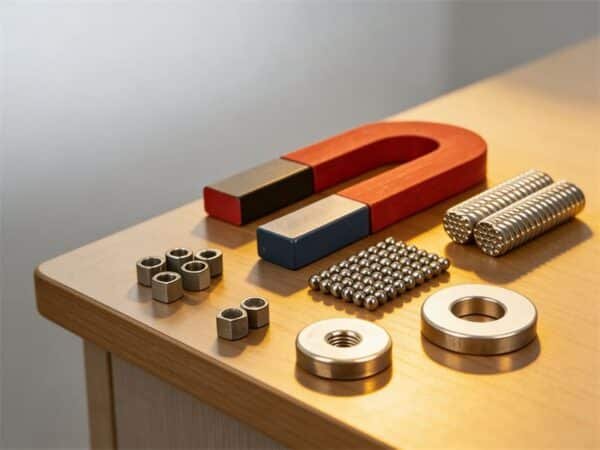
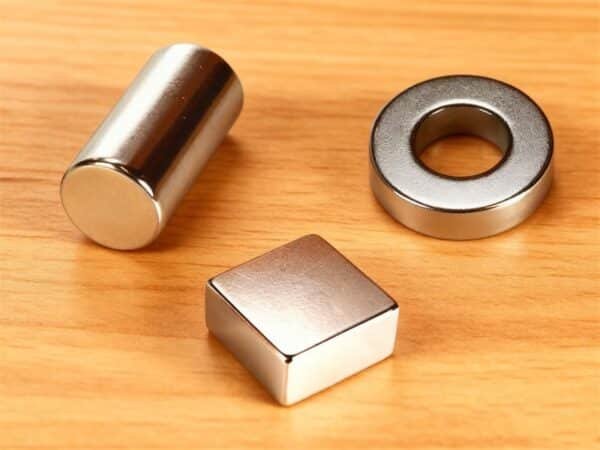
Many people ask me, what is a disc magnet? A disc magnet is a round, flat magnet with strong magnetic fields focused on its flat surfaces. These magnets look simple, but their shape makes them stand out. Understanding magnetic field basics helps you see why disc magnets work so well in daily life. I see disc magnets everywhere:
- 🧲 They hold signs, close packaging, and secure items in electronics.
- 💼 They filter metal in factories and keep things in place in machinery.
Disc magnets use their magnetic field to make tasks easier and more reliable.
What is a Disc Magnet
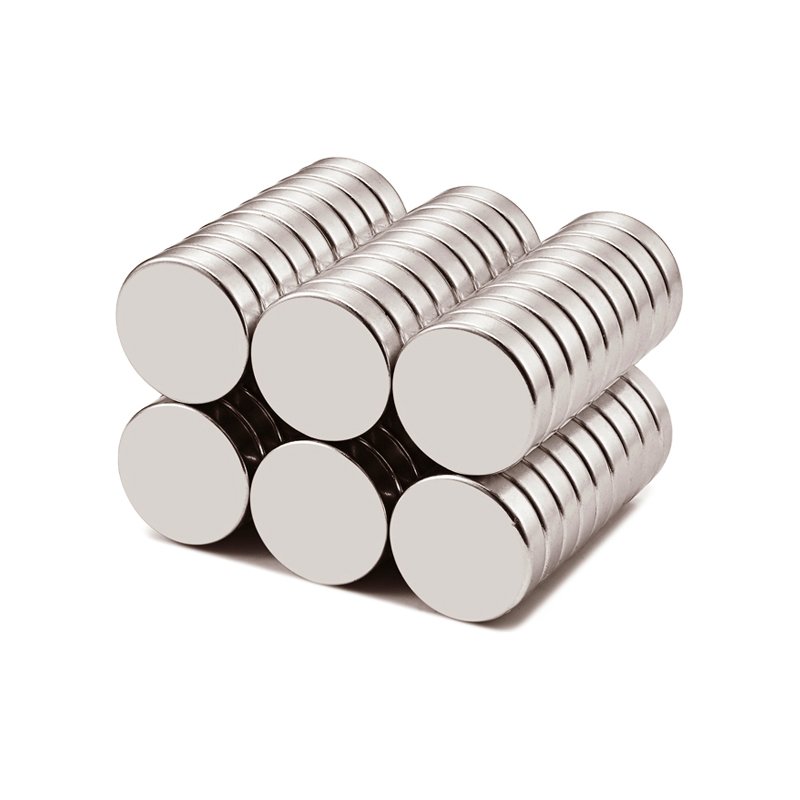

A disc magnet is a flat, round magnet with a diameter greater than its thickness. People often ask me about disc magnets. The answer is easy, but details are important. When I hold one, it feels thin and wide. It is different from other magnets. The flat sides make it pull strongly on both faces.
Here are some main things I notice about a disc magnet:
- 🟢 It is flat and shaped like a disk with a big, round surface.
- 🟢 The diameter is always bigger than how thick it is.
- 🟢 It is made from strong materials like neodymium, ferrite, samarium-cobalt, or alnico.
- 🟢 It has strong magnetic fields that focus on the flat sides.
- 🟢 It is used in motors, sensors, speakers, and many other things.
- 🟢 It is simple to use and lasts a long time.
- 🟢 You can find them in many sizes and grades for different jobs.
When I think about what makes a disc magnet special, I see that the shape helps make a strong, focused magnetic field. This is why disc magnets work well for holding, attaching, or sensing things.
Disc Magnets vs Other Shapes
I like to compare disc magnets to other types so people can see what makes them unique. Each magnet shape has its own uses and features. Here is a table I use to show the differences:
| Magnet Shape | Structure | Magnetic Field | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disc Magnet | Flat, round, wide pole area | Strong, focused at center | Holding, crafts, electronics |
| Bar Magnet | Long, rectangular | Field lines spread out | Sensing, separation, classrooms |
| Ring Magnet | Circular with a hole | Less strength, hollow center | Motors, sensors, rotating devices |
| Cylinder Magnet | Round, tall | Uniform, reliable field | Sensors, actuators, industry |
| Horseshoe Magnet | U-shaped, close poles | Very strong, small area | Lifting, engineering, science demos |
💡 I always tell my friends that disc magnets are special because their flat, round shape gives them a strong pull right where you need it. Other magnets, like bar or ring magnets, spread their force in other ways or work best in certain setups.
Disc magnets are the shape I see most in stores and factories. Their features make them useful and not too expensive. I use them for fixing things or making small machines. When someone asks me about disc magnets, I show how the shape and features make them so helpful.
Magnetic Fields of Disc Magnets
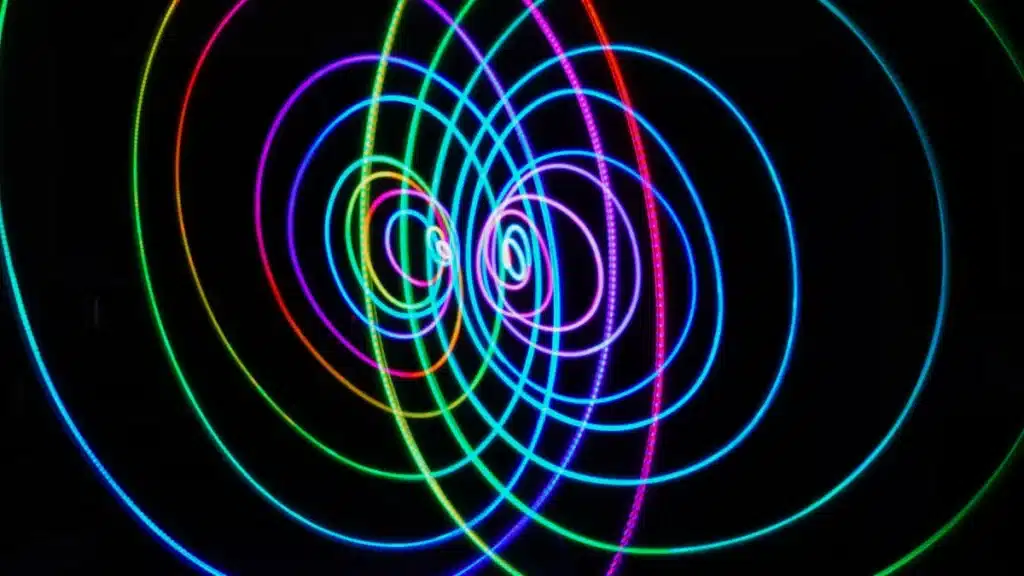

Field Structure
Disc magnets produce a magnetic field that is strongest at the flat surfaces and spreads out in a three-dimensional pattern. When I look at a disc magnet, I notice the magnetic field lines start at one flat side. They curve around to the other flat side. This makes a strong magnetic field in the middle of each face.
Here’s what I see about the field structure of disc magnets:
- The magnetic field lines are packed tightly at the center of the flat sides.
- The field is strongest near the surface and even more at the edges. Edge effects make the field stronger there.
- The magnetic field lines loop from one side to the other. This makes a clear path for attracting or pushing away other magnets.
- The field is not just flat. It goes above, below, and around the magnet. This makes it three-dimensional.
- The magnetic flux lines show how the field moves through and around the disc magnet.
🧲 Tip: If you put iron filings on a disc magnet, you can see the magnetic field lines. They make cool patterns, especially at the edges!
Field Strength
The field strength of disc magnets depends on their material, thickness, and size, with neodymium disc magnets showing the strongest magnetic properties. I always check the grade and thickness when I want a strong magnet. Thicker disc magnets have a stronger field at the surface. Thinner ones are weaker.
📏 Note: Modern sensors make it easy to check field strength. Old ways, like using a compass or magnetic pendulum, can also show how strong a magnet is.
Field Distribution
Disc magnets have a concentrated magnetic field at their faces, but the field spreads out and weakens with distance, especially compared to bar magnets. I see the field is not the same everywhere around the magnet. The strongest pull is at the center and edges of the flat sides.
Here’s a table to help you see how the magnetic field distribution of disc magnets compares to other shapes:
| Magnet Shape | Magnetic Field Lines Pattern | Field Distribution | Attracting/Repelling Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disc Magnet | Lines loop from face to face | Concentrated at faces and edges | Strong attracting and repelling |
| Bar Magnet | Lines spread from end to end | More spread out, less focused | Good for attracting, less for repelling |
| Ring Magnet | Lines loop through center hole | Uniform around ring, less at center | Balanced attracting and repelling |
🌀 Fun Fact: The magnetic field lines of disc magnets can look different if the magnet is magnetized in different ways. This changes how the field moves and how the magnet works with other magnets.
Shape and Size Impact
Thickness
Thicker disc magnets have stronger magnetic fields and a longer reach than thinner ones of the same diameter. When I use a thick disc magnet, I notice its strong pull right away. The extra thickness means there is more magnetic material inside. This makes the magnetic field stronger. As the magnet gets thicker, it can hold heavier things. But after a certain thickness, making it even thicker does not help much. For example, I tried a 1/2″ diameter disc magnet with different thicknesses. The thicker magnets could hold more weight. But adding even more thickness did not make a big difference. The surface the magnet sticks to also matters. If the steel is too thin, the magnet cannot work as well.
🧲 Tip: If you want to hold heavy things, pick a thicker disc magnet. But super thick magnets may not always be much stronger.
Diameter
A larger diameter increases the holding force of disc magnets by giving them a bigger surface area and more magnetic flux. I always check both thickness and diameter for strong magnetic properties. A bigger diameter lets the magnet touch more metal. This helps the magnetic field spread out and grab better.
When I use disc magnets with a bigger diameter, I see a big jump in holding power. The magnetic field covers more area. This means stronger magnetic properties and better results for holding, attaching, or sensing.
Comparison to Other Magnets
Disc magnets stand out because their wide, flat shape creates strong, focused magnetic fields, making them versatile and powerful for many uses. I like to compare disc magnets to cube and cylinder magnets. This helps people pick the right one.
Here’s a table that shows the differences:
| Magnet Shape | Key Characteristics | Performance Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Disc Magnets | Wide, flat surface; low profile | Strong and effective due to broad contact area; versatile; sometimes tricky to handle |
| Cube Magnets | Equal sides; easy to grip | Good for simple uses; poles are harder to spot |
| Cylinder Magnets | Tall, round; easy to grasp | Strong pull along the center; great for focused magnetic fields |
I see that disc magnets and cylinder magnets both have strong magnetic fields along their axis. Disc magnets are best when I need a flat, wide area to stick to something. Cylinder magnets are better for a strong pull in one direction. Cube magnets are easy to hold but do not always have the same strong magnetic properties as disc magnets.
💡 Note: I choose disc magnets when I need a strong, flat magnet for holding or sensing. Their features make them a great choice for many projects.
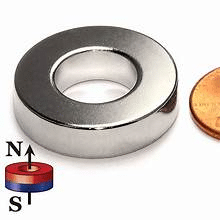
Difference between Ring Magnet and Disc Magnet
Center Hole
The biggest difference between a ring magnet and a disc magnet is the center hole.
A ring magnet has a hole in the middle. A disc magnet does not have a hole. The ring magnet’s hole makes it useful in special ways. The disc magnet is solid, so it works differently.
🕳️ Tip: I use ring magnets when I need to put a magnet over a rod or screw. I use disc magnets when I want a strong, flat magnet to hold things.
Magnetic Field Orientation
Ring magnets and disc magnets have different magnetic field patterns because of their shapes.
The ring magnet’s hole changes how the magnetic field moves. The field goes around the hole and spreads out from the edge. The disc magnet’s field goes straight through the flat sides. This makes the pull strong and even on the faces.
🧲 When I use ring magnets, they can attract or push other magnets from farther away, mostly near the edge. Disc magnets pull hard right on the flat side, which is good for holding or sensing.
Common Applications
Ring magnets and disc magnets work best in different jobs because of their shapes and magnetic fields.
I use ring magnets when I need to slide them onto rods or use them in motors. The hole lets me do things disc magnets cannot. Here are some places where I use each type:
- Ring Magnet Applications:
- Speakers and sensors 🎤
- Motors and car parts 🚗
- Magnetic bearings for less friction ⚙️
- Science experiments with magnets 🧪
- Disc Magnet Applications:
- Holding things on metal at home 🏠
- DIY crafts and projects ✂️
- Electronics and fixing furniture 💡
- Any job needing a strong, flat magnet for pulling or pushing
Materials
Neodymium
Neodymium magnets are the strongest type of disc magnets you can find. I use these when I need a small magnet with big strength. They are made from neodymium, iron, and boron mixed together. Most neodymium disc magnets have a nickel, zinc, or epoxy coating. This stops them from rusting. I see neodymium disc magnets in electronics, motors, jewelry, and school science projects.
Here’s why I like neodymium magnets:
- 🏋️♂️ They are super strong, even when very small.
- 🛡️ They need a coating to keep away rust.
- 🔥 They work best below 80°C, but some can go up to 200°C.
- 💡 They are great when space is tight but strength is needed.
Tip: I am always careful with neodymium magnets. They can snap together fast and might break if I am not careful.
Ferrite
Ferrite disc magnets are tough, affordable, and work well in many everyday uses. I pick ferrite magnets when I need one that can handle water or heat. They are made from iron oxide and barium or strontium carbonate. Ferrite magnets do not rust, so I use them outside or in wet places.
Material Effects
The material you pick for disc magnets changes how strong they are and how much heat they can handle. I always think about where I will use the magnet before picking the material. Neodymium gives the most power, but ferrite is better for wet or hot places.
🧲 Note: I always match the magnet material to the job. For example, I use neodymium for strong holding in gadgets, and ferrite for outdoor or high-temperature uses.
uses of disc magnet
Disc magnets have a variety of applications because of their strong, focused magnetic fields and compact shape. I see disc magnets in many places. They are in small gadgets and big machines. I use them often in my daily life and work.
Industrial Uses
Disc magnets are essential in many industrial applications. I see them used for lifting, holding, and moving metal parts. In factories, disc magnets help separate iron and steel from other things. This makes products safer and cleaner.
Here’s a quick list of how I use disc magnets in industry:
- 🏭 Lifting and holding metal parts during assembly
- 🤖 Automation and robotics systems for precise movement
- 🧲 Magnetic separation in food processing, recycling, and mining
- ⚙️ Motors, actuators, and magnetic couplings in machines
- 🔩 Fixturing and workholding to keep pieces steady
I also use disc magnets in robot tools. These magnets grab and let go of parts fast. This makes production lines quicker and safer. Their strong fields and small size help make machines smaller and work better.
💡 Tip: If you want to organize your space, try disc magnets. They can help in many ways!
In summary, the variety of applications for disc magnets covers electronics, industry, and home life. Their strong pull, small size, and easy handling make them a top choice for many jobs.
Medical Uses
Disc magnets play a big role in modern medicine. Hospitals and clinics use these magnets in many ways. Their strong, focused magnetic fields help doctors and engineers make better treatments.
Here are some common ways disc magnets are used in medicine:
- 🧲 MRI Machines: These machines use strong magnets to take clear pictures inside your body. Disc magnets help make the magnetic field needed for these images.
- 💊 Magnetic Drug Targeting: Doctors use magnets to move tiny medicine particles to the right spot. This helps treat sickness with fewer side effects.
- 👂 Cochlear Implants: Disc magnets hold hearing device parts together. This makes it easy to put on and take off hearing aids.
- 🦷 Dental Implants: Some dental tools use magnets to keep dentures or crowns in place. This helps them fit well and makes eating easier.
- 🦴 Orthopedic Devices: Magnets can help bones heal by sending signals for bone growth. I have seen them in special braces and bone healing tools.
- 🩺 Magnetic Navigation in Surgery: Surgeons use magnets to guide tools inside the body. This helps with heart surgery and other careful operations.
- ⌚ Wearable Health Devices: Many health trackers use magnetic sensors to check your heart rate or movement.
Note: There are many uses for disc magnets in medicine, but safety is always most important. Doctors and engineers work together to make sure these magnets are safe for patients.
Why Choose OSENC
Expertise
I choose OSENC because they are true experts in neodymium magnets and magnetic assemblies. I have watched their team work on many projects. They always show skill and care. Here are some things I notice:
- OSENC has neodymium magnets in lots of sizes and thicknesses. I can always find the one I need.
- They offer coatings like zinc, nickel, silver, gold, and epoxy. These coatings help protect the magnet in any place.
- I can ask for custom disc magnets. They make regular shapes in 7 days and custom ones in 20 days.
- Their engineers help me with special designs and different magnetization directions. They also make magnets with adhesive backs or countersunk holes.
- OSENC has finished over 300 custom neodymium magnet projects. They work with car, airplane, medical, and electronics companies.
🧲 I trust OSENC because they care about quality and new ideas. They also ship fast, which helps my projects.
Quality
OSENC takes quality seriously at every step. I feel safe using their magnets because they check everything. Here is what they do:
- Quality engineers check the materials, how they are made, and the finished magnets.
- They use special tools to test strength, size, and coating. Some tools are gauss meters, permeameters, and salt spray chambers.
- Every shipment follows IATA safety rules. I never worry about getting my order.
- OSENC has ISO 9001 certification. This means they follow strict quality rules.
- They only buy from certified suppliers and use the best neodymium magnets.
- Their team always tries to get better and never skips steps.
✅ I know OSENC will give me strong, high-quality magnets every time.
Choosing the Right Disc Magnet
Size
I always start by picking the right size for my project. The size of a disc magnet can make a big difference in how well it works. Here’s what I look at when choosing:
- 🧲 Application Needs: I think about what I want the magnet to do. Does it need to fit in a small space? Will it be used for attracting metal parts or holding something in place?
- 📏 Space and Weight: I check if there’s enough room for the magnet. If I need a lightweight option, I go for a thinner or smaller disc.
- 🛠️ Assembly: I make sure the magnet is easy to put in place. If it’s too big, it might not fit. If it’s too small, it might not be strong enough.
- 🌡️ Environment: I consider if the magnet will face heat, moisture, or rough handling. Some magnets need special coatings to last longer.
- 💡 Testing: I like to test the magnet in real conditions. This helps me see if it really works before I use it for good.
Tip: I sometimes use magnetic field simulation tools to check if the size and shape will work before I buy a bunch of magnets.
Strength
I always match the magnet’s strength to the job. If I need a magnet for attracting heavy objects, I pick one with higher pull force. Here’s how I figure out the right strength:
- 💪 Material: Neodymium magnets are much stronger than ceramic ones. I use neodymium when I need a lot of power in a small size.
- 📐 Size and Shape: A bigger disc usually means more strength. The disc shape helps focus the magnetic field, which is great for attracting things right on the flat face.
- 🔥 Temperature: I check if the magnet will get hot. High temperatures can make some magnets weaker.
- 🏷️ Grade: I look at the magnet’s grade, like N42 or N52. Higher numbers mean more strength, but sometimes I pick a lower grade if I need better heat resistance.
- 🧪 Testing: I measure pull force or use a gaussmeter to check the field strength. This helps me know if the magnet will do the job.
Safety
I never skip safety when working with disc magnets. They can be powerful and sometimes dangerous if not handled right.
Alert: Never try to cut, grind, or heat a magnet. It can shatter or even explode!
By following these steps, I make sure my magnets stay safe, strong, and ready for any attracting job I need.
Disc magnets stand out for their strong, focused magnetic fields and simple shape. I use them in electronics, industry, and even at home. Here’s what I always remember:
- 🧲 Disc magnets work best when I need a strong, flat pull.
- 💡 Their size and material change how they perform.
- 🚀 Osenc gives me quality, variety, and expert help every time.
When I pick a disc magnet, I always think about my project’s needs. That way, I get the best results!
FAQ
What is the strongest type of disc magnet?
Neodymium disc magnets are the strongest.
I always pick neodymium when I need maximum holding power. These magnets pack a lot of strength into a small size. They work great for tough jobs in electronics, crafts, and industry. 🏋️♂️
Can disc magnets lose their magnetism?
Yes, disc magnets can lose magnetism.
If I heat them too much, drop them hard, or store them near strong magnetic fields, they can get weaker. I always handle my magnets with care to keep them strong. 🔥❌
How do I safely store disc magnets?
I store disc magnets in a non-magnetic box with spacers.
I keep them away from electronics, credit cards, and kids. I also separate strong magnets with cardboard or foam to prevent them from snapping together. 📦🧲
Are disc magnets safe for kids?
No, disc magnets are not safe for kids.
Swallowing magnets can cause serious injury. I always keep magnets out of reach of children and pets. Safety comes first! 🚸

I’m Ben, with over 10 years in the permanent magnet industry. Since 2019, I’ve been with Osenc, specializing in custom NdFeB magnet shapes, magnetic accessories, and assemblies. Leveraging deep magnetic expertise and trusted factory resources, we offer one-stop solutions—from material selection and design to testing and production—streamlining communication, accelerating development, and ensuring quality while reducing costs through flexible resource integration.