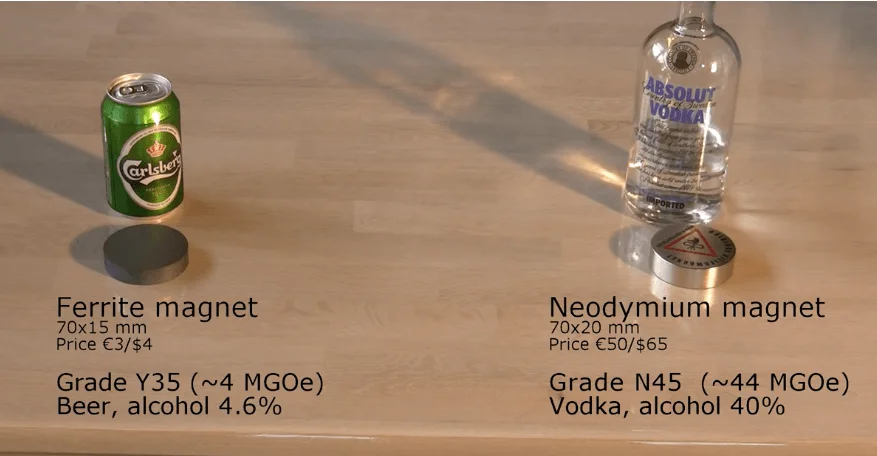
Magnets come in different shapes and sizes, and when shopping for neodymium magnets, you may come across the term “grade,” which refers to the strength of the magnetic material used in the magnet. Understanding the grades of magnets can help you choose the right one for your specific application.
What Are Magnet Grades?
Magnet grades are a measurement of the magnetic strength of the magnet, which is indicated by a capital N followed by a two-digit number and sometimes extra letters. The N stands for Neo, which is short for neodymium, one of the four types of magnets commercially available. The number after the N indicates the maximum energy product in MGOe, which is the maximum strength of the magnetic material. The higher the number, the stronger the magnet. But, there is a range for each grade of neodymium magnet.
Neodymium Magnet Strength Chart
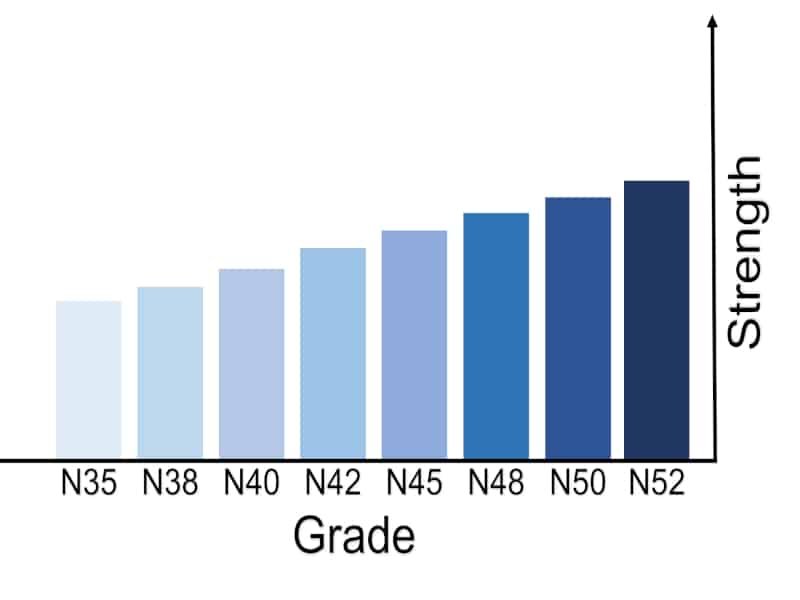
N45 vs N52
For example, the final energy product for an N45 magnet strength can range from 43-46 MGOe. N52 range from 49-52 MGOe. That is why an N52 magnet must be stronger than an N44 magnet of the same size and shape. Because the N52 neodymium magnet has greater magnetic strength than the N45 magnet. (Related: n35 vs n52 magnet)
N50 vs N52 Magnets
Grade N50 magnets must not be stronger than 52 magnets’ strength. Because the range of N50 is 47-51 MGOe. There are some ranges that are the same as N52.
Related: N42 Vs N45 Vs N52 Magnet
How Do Magnet Grades Affect Magnet Strength?
The magnet strength rating depends on several factors, including its size, shape, and the magnetic material used. Although the magnet strength scale is an important factor, it’s not the only factor that determines the strength of a magnet. For instance, two magnets of the same size and shape but with different grades may have a strength difference of anywhere between 11-21% or even lower. As a practical rule of thumb, there’s 1% more pull force for every extra MGOe. So, an N52 magnet is about 7% stronger than an N45 magnet of the same size and shape. ( The pull force of big size N45 is bigger than the small size N52 magnet.)
Related: How strong are neodymium magnets
Do all kind magnets use the same grade system?
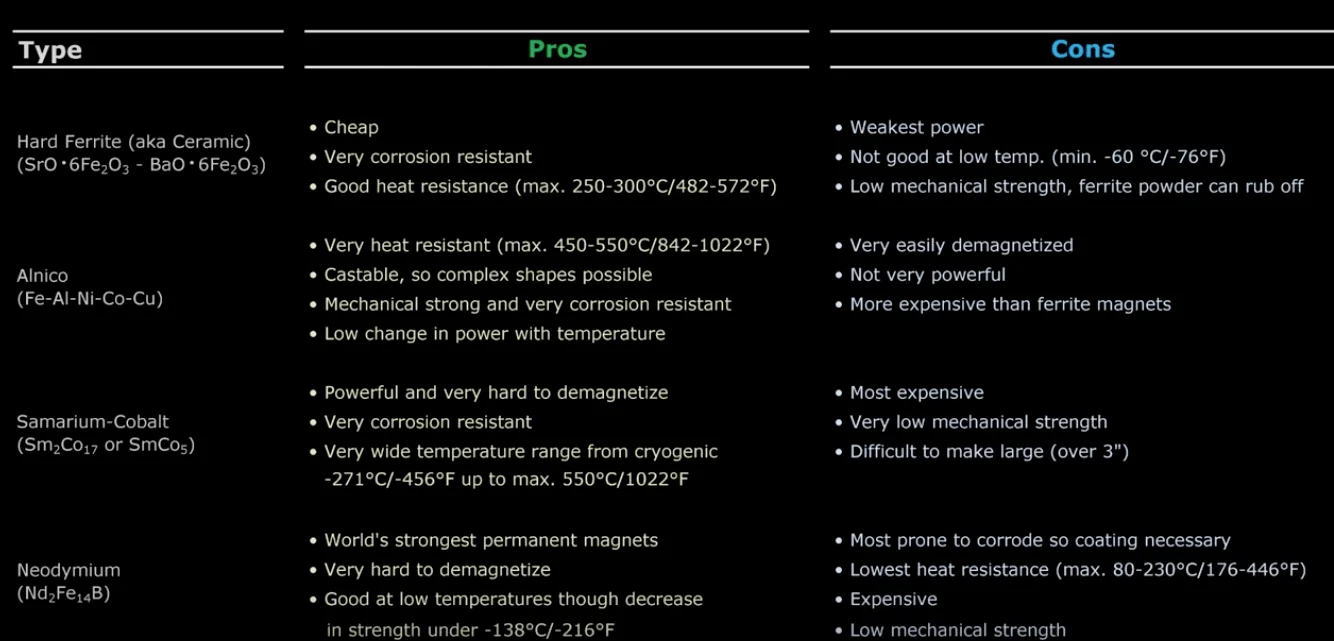
No, the grades of ferrite, SmCo, and neodymium magnets are not the same. Each type of magnet has its own grading system based on its magnetic properties such as strength, maximum energy product, coercivity, and temperature stability.
For example, neodymium magnets are graded based on their maximum energy product (BHmax) which is a measure of their magnetic strength. The higher the grade (such as N52), the stronger the magnet. SmCo magnets are graded based on their maximum energy product and temperature stability, while ferrite magnets are graded based on their magnetic flux density and coercivity.
Therefore, it’s important to choose the appropriate magnet type and grade based on the specific application requirements.
Extra Letters On Neodymium Magnet Grades
Sometimes, magnet grades have extra letters at the end of the grading, which indicate how well the magnet can withstand high temperatures. The standard neodymium magnets can generally withstand temperatures up to 80°C. If heated above this, they will lose some of their magnetic strength even after being cooled down. In contrast, neodymium magnets with extra letters can withstand higher temperatures, up to 150°C, for instance. However, they are generally weaker and more expensive.
Magnet specifications
Material | Remanence | Coercivity | Energy- product | Max. Temperature | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br | bHc | iHc | (BxH)max | ||||||
| Gauss (G) | Tesla (T) | kOe | k/m | kOe | k/m | MGOe | kJ/m³ | °C | |
| N30 | 10800-11200 | 1.08-1.12 | 9.8-10.5 | 780-836 | ≥ 12 | ≥ 955 | 28-30 | 223-239 | ≤ 80 |
| N33 | 11400-11700 | 1.14-1.17 | 10.3-11.0 | 820-876 | ≥ 12 | ≥ 955 | 31-33 | 247-263 | ≤ 80 |
| N35 | 11700-12100 | 1.17-1.21 | 10.8-11.5 | 860-915 | ≥ 12 | ≥ 955 | 33-35 | 263-279 | ≤ 80 |
| N38 | 12200-12600 | 1.22-1.26 | 10.8-11.5 | 860-915 | ≥ 12 | ≥ 955 | 36-38 | 287-303 | ≤ 80 |
| N40 | 12600-12900 | 1.26-1.29 | 10.5-12.0 | 860-955 | ≥ 12 | ≥ 955 | 38-40 | 303-318 | ≤ 80 |
| N42 | 12900-13200 | 1.29-1.32 | 10.8-12.0 | 860-955 | ≥ 12 | ≥ 955 | 40-42 | 318-334 | ≤ 80 |
| N45 | 13200-13700 | 1.32-1.37 | 10.8-12.5 | 860-995 | ≥ 12 | ≥ 955 | 43-45 | 342-358 | ≤ 80 |
| N48 | 13700-14200 | 1.37-1.42 | 10.8-12.5 | 860-995 | ≥ 12 | ≥ 955 | 45-48 | 358-382 | ≤ 80 |
| N50 | 14000-14600 | 1.40-1.46 | 10.8-12.5 | 860-995 | ≥ 12 | ≥ 955 | 47-51 | 374-406 | ≤ 80 |
| N52 | 14200-14700 | 1.42-1.47 | 10.8-12.5 | 860-995 | ≥ 12 | ≥ 955 | 48-53 | 380-422 | ≤ 80 |
Conculsion
The grade of a magnet is a crucial factor in determining its strength, but it’s not the only factor. When shopping for magnets, it’s important to consider the size, shape, and magnetic material used, in addition to the grade. Neodymium magnets are generally stronger than ferrite magnets and come in different grades, each with its own maximum energy product. Additionally, the extra letters at the end of the grading indicate how well the magnet can withstand high temperatures. By understanding the grades of magnets, you can make an informed decision on which magnet to choose for your specific application.
FAQ
Neodymium magnet n52 strength
Neodymium magnet
N52 strength range from 49-52 MGOe.
How are magnets rated
Magnets are rated by their grade, pull force, surface strength, and material. The grade (like N35 or N52) shows how strong the magnet is—the higher the number, the stronger the magnet. Pull force tells how much weight the magnet can hold. Surface strength is measured in Gauss and shows how strong the magnet is at the surface. Material also matters—neodymium is very strong, ceramic is weaker but cheaper. Some magnets can lose strength if they get too hot.
N52 magnet meaning
An N52 magnet is a very strong neodymium magnet. The “N” means neodymium, and “52” is the grade. The higher the number, the stronger the magnet. N52 is one of the strongest types, so even a small N52 magnet can hold a lot of weight.

I’m Ben, with over 10 years in the permanent magnet industry. Since 2019, I’ve been with Osenc, specializing in custom NdFeB magnet shapes, magnetic accessories, and assemblies. Leveraging deep magnetic expertise and trusted factory resources, we offer one-stop solutions—from material selection and design to testing and production—streamlining communication, accelerating development, and ensuring quality while reducing costs through flexible resource integration.