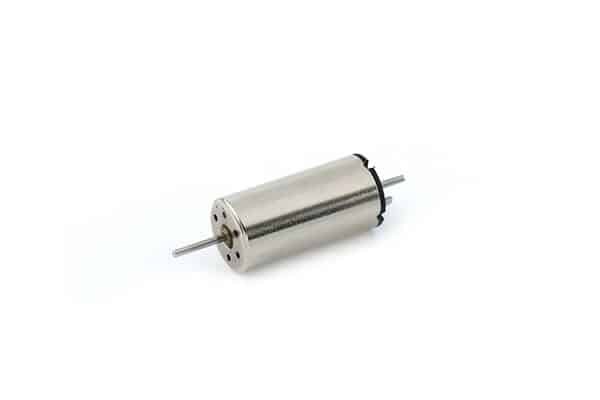
A coreless motor is a lightweight, high-performance DC motor that replaces the traditional iron core with a hollow, self-supporting coil design, reducing inertia and eliminating iron losses. This structure delivers rapid acceleration, smooth rotation without cogging, and excellent efficiency. Widely used in robotics, drones, medical devices, and precision instruments, coreless motors are ideal for applications requiring quick response, compact size, and high power-to-weight ratios.
I’ve been asked a lot about coreless motors, so we’ve written an article to explain. In this article, we’ll explain what a coreless motor is, how it functions, and why it’s gaining traction in various industries.
What is a Coreless Motor

A coreless motor, also known as a hollow cup motor. A coreless motor is a lightweight, high-performance DC motor that replaces the traditional iron core with a hollow, self-supporting coil design, reducing inertia and eliminating iron losses. This structure delivers rapid acceleration, smooth rotation without cogging, and excellent efficiency. Widely used in robotics, drones, medical devices, and precision instruments, coreless motors are ideal for applications requiring quick response, compact size, and high power-to-weight ratios.
Basic Structure

The basic structure of a coreless motor can be broken down into a few key parts:
- Rotor (Armature)
- Made of a hollow, basket-shaped coil winding with no iron core.
- Very light and thin, reducing inertia and allowing fast response.
- Permanent Magnets
- Fixed to the stator housing (outer casing).
- Provide the magnetic field that interacts with the rotor winding.
- Commutator & Brushes
- Supply current to the rotor coil.
- Often made of precious metals (like silver or gold alloy) to ensure low resistance and long life.
- Shaft & Bearings
- The motor shaft runs through the center, supported by precision bearings for smooth rotation.
Coreless Motor Working Principle
👉 In essence: A coreless motor works by letting current flow through a lightweight, ironless winding that interacts with the stator’s permanent magnetic field, creating continuous torque and enabling high efficiency, fast acceleration, and smooth motion.
- Current Flow in the RotorWhen DC current flows through the hollow “basket” winding, it generates a magnetic field around the rotor.
- Lorentz Force ActionThe magnetic field from the rotor interacts with the permanent magnet field fixed in the stator.According to the Lorentz force law, a force is exerted on the conductors, producing torque that makes the rotor spin.
- CommutationAs the rotor turns, the commutator and brushes automatically switch the current direction in the windings.This keeps the torque continuous and the rotor spinning smoothly.
- No Iron Core AdvantageSince there is no iron in the rotor, there’s no cogging torque or eddy current losses, leading to smooth, efficient, and fast response.
Applications of Coreless Motors
🤖 Robotics
- Core Advantages: Low inertia + Fast response
- Benefits:
- Extremely quick acceleration and deceleration for dynamic motion control.
- Smooth torque output without cogging, ensuring stable joint movements.
- High positioning accuracy, ideal for complex trajectories.
- Typical Applications: Robotic arms, surgical robots, UAV propulsion motors.
✈️ Aerospace
- Core Advantages: Lightweight + High efficiency + High reliability
- Benefits:
- High power density, delivering strong output within strict weight limits.
- Low heat generation and energy consumption, extending battery life.
- Stable performance even under extreme temperature and vibration conditions.
- Typical Applications: UAV propulsion, satellite attitude control actuators, electric aircraft auxiliary systems.
🏥 Medical Devices
- Core Advantages: Low noise + Smooth operation + High precision
- Benefits:
- Quiet and vibration-free operation, ideal for medical environments.
- Accurate and reliable motion control for safe drug delivery or surgical tools.
- Compact size, suitable for portable or implantable devices.
- Typical Applications: Infusion pumps, cardiac assist pumps, surgical robots, medical imaging platforms.
🏭 Industrial Automation
- Core Advantages: Fast response + High precision control
- Benefits:
- Enhances production speed and automation efficiency.
- Suitable for high-precision manufacturing and micron-level machining.
- Energy-efficient operation, reducing factory energy costs.
- Typical Applications: CNC machine spindles, conveyors, dispensing systems, automated assembly lines.
🏠 Household Appliances
- Core Advantages: Compact design + Low noise
- Benefits:
- Enables smaller and more portable products.
- Quiet operation improves user comfort.
- High efficiency, extending battery life in portable devices.
- Typical Applications: Electric toothbrushes, shavers, coffee grinders, smart vacuum cleaners.
🚗 Automotive
- Core Advantages: High responsiveness + Durability
- Benefits:
- Provides precise and responsive control of electric components in vehicles.
- Withstands high temperatures, vibrations, and long-term operation.
- Compact and lightweight, supporting vehicle weight reduction.
- Typical Applications: Fuel injection pumps, headlight adjusters, power seats, mirror control systems.
🎯 Precision Instruments
- Core Advantages: Zero cogging + Smooth rotation
- Benefits:
- Ensures extremely high accuracy and stability.
- Low noise and minimal electromagnetic interference, ideal for sensitive measurement systems.
- Small form factor allows integration into compact precision devices.
- Typical Applications: Camera autofocus/zoom, watch movements, scientific measuring instruments.
Coreless Motor Feature

🔹 Compact Structure
Coreless motors eliminate the traditional iron core, using a self-supporting coil design. This makes them smaller and more compact while still delivering high output power. Their compact structure is ideal for devices where space is limited, such as drones, medical equipment, and precision instruments.
🔹 Light Weight
Without the iron core, coreless motors are significantly lighter than traditional motors. The reduced weight not only improves efficiency but also enhances portability, making them a preferred choice in aerospace, robotics, and handheld devices.
🔹 High Speed and Efficiency
The absence of iron losses allows coreless motors to achieve extremely high rotational speeds with excellent efficiency. They respond quickly to control signals, making them perfect for high-performance applications like robotic arms, drones, and automotive components.
🔹 Low Noise
The smooth electromagnetic design reduces cogging torque and vibrations, resulting in quieter operation. This makes them suitable for medical devices, precision instruments, and household appliances where silent performance is critical.
🔹 Stability
Coreless motors provide smooth and stable rotation even at low speeds, thanks to the absence of cogging. This stability ensures accurate control and positioning, especially in robotics, automation, and optical instruments.
🔹 High Reliability
The simplified structure with fewer magnetic losses and lower heat buildup increases reliability. Coreless motors can operate consistently under demanding conditions, making them suitable for aerospace and automotive systems.
🔹 Long Life
With lower wear and tear on components, reduced mechanical stress, and efficient thermal performance, coreless motors typically offer a longer lifespan compared to traditional motors. This durability reduces maintenance needs and enhances long-term performance.
Classifications of Coreless Motors
1. Brushed Coreless DC Motors
- Use commutator and brushes to switch current in the rotor winding.
- Simple, compact, and widely used in toys, medical devices, and small electronics.
- Advantages: low inertia, smooth operation, low cost.
- Limitation: brush wear reduces lifetime.
2. Brushless Coreless DC Motors (BLDC)
- Use electronic commutation instead of brushes.
- Rotor is coreless winding or permanent magnets, and stator has coils.
- Longer lifespan, higher efficiency, less maintenance.
- Common in drones, robotics, aerospace, and precision equipment.
3. Coreless Servo Motors
- Specifically designed for precise control of position, speed, or torque.
- Integrated with encoders or feedback systems.
- Used in robot joints, CNC machines, and medical robotics.
4. Coreless Stepper Motors
- Operate in discrete steps for accurate positioning.
- Coreless design reduces inertia, allowing very fast response.
- Applied in 3D printers, camera focusing systems, and optical equipment.
DC Coreless Motor vs. Traditional DC Motor
A DC coreless motor offers faster response, higher efficiency, and smoother motion, but at higher cost and lower durability (for brushed versions). A traditional DC motor is more rugged and economical, but heavier and less responsive.
⚙️ 1. Rotor Construction
- Coreless Motor: Rotor is a hollow, basket-shaped coil with no iron core.
- Traditional DC Motor: Rotor has iron laminations with copper windings.
⚡ 2. Inertia & Response
- Coreless Motor: Very low inertia, enabling fast acceleration and deceleration.
- Traditional DC Motor: Higher inertia due to heavy iron core, making response slower.
🔄 3. Torque Characteristics
- Coreless Motor: Smooth torque, no cogging (no magnetic teeth effect).
- Traditional DC Motor: Cogging torque present, especially at low speeds.
🔋 4. Efficiency & Heat
- Coreless Motor: High efficiency; no iron losses (eddy current/hysteresis).
- Traditional DC Motor: Lower efficiency due to iron losses and heat buildup.
🛠️ 5. Size & Weight
- Coreless Motor: Lightweight and compact, ideal for portable or space-limited devices.
- Traditional DC Motor: Heavier and bulkier.
🧩 6. Durability & Cost
- Coreless Motor: Brushes (in brushed type) wear quickly; generally more expensive.
- Traditional DC Motor: More robust and cheaper, with longer brush life in many cases.
📌 7. Applications
- Coreless Motor: Robotics, drones, medical devices, cameras, aerospace—where precision, speed, and lightweight are crucial.
- Traditional DC Motor: Fans, pumps, conveyors, industrial machines—where durability and cost-efficiency matter.
Reference:

I’m Ben, with over 10 years in the permanent magnet industry. Since 2019, I’ve been with Osenc, specializing in custom NdFeB magnet shapes, magnetic accessories, and assemblies. Leveraging deep magnetic expertise and trusted factory resources, we offer one-stop solutions—from material selection and design to testing and production—streamlining communication, accelerating development, and ensuring quality while reducing costs through flexible resource integration.