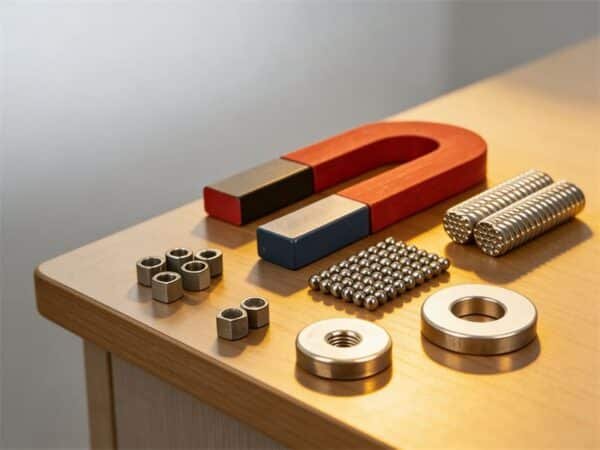
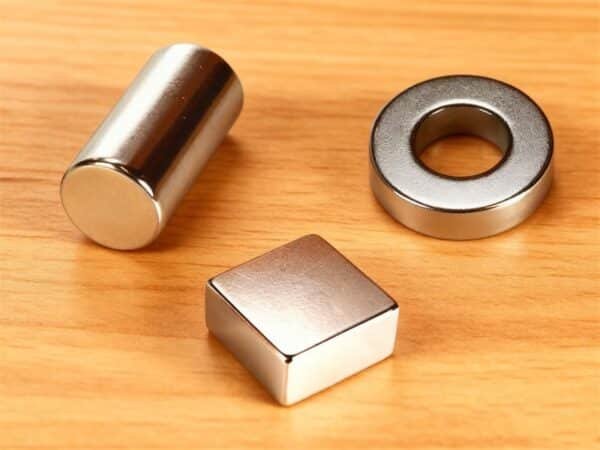
Magnets have been of interest to the human race since the early civilizations of human beings, when naturally occurring magnetic stones were discovered, and continue to be of interest in our modern world of sophisticated engineered magnets. They are essential in modern technology, driving household devices to complex scientific machines.
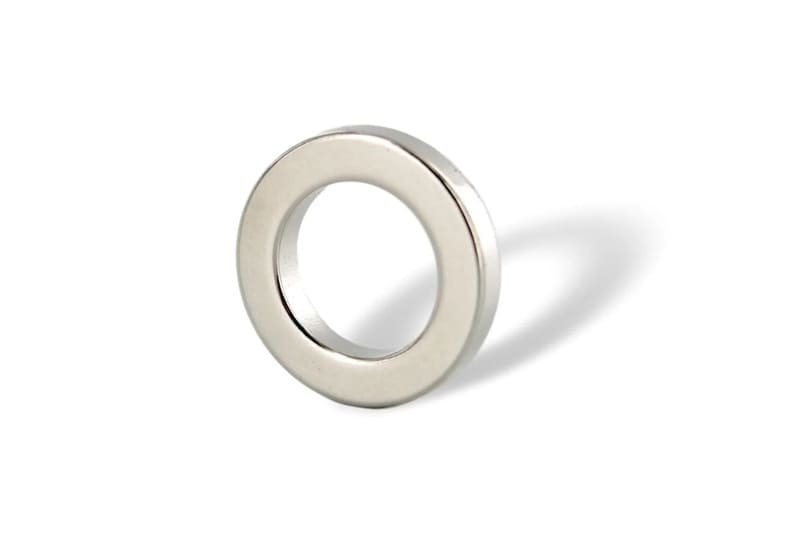

What Are Ring Magnets?
A ring magnet, as the name implies, is a ring-shaped, or rather a donut-shaped, magnet, hollow in the middle. This is not simply a design. The hole lets you slide the magnet over a rod or shaft so the magnetic field can work around that center. This shape is handy in small motors, generators, and magnetic couplings (devices that pass motion without touching). Ring magnets come in many diameters and thicknesses.
Compared to ordinary bar magnets or block magnets, ring magnets permit a shaft, rod, or screw to run through the centre of them, without impairing their magnetic capability. This qualifies them as a good option in motors, generators, loudspeakers, medical equipment, and scientific devices.
Ring magnets are a solution of choice in both renewable energy and consumer electronics because of their pull strength, versatility, and size.
Ring Magnet Features and Characteristics

Ring magnets can be seen as something simple, but they possess special characteristics that make them special. These are their main features and characteristics broken down into details:
Shape & Structure
The hollow center is not a waste of material; it can be conveniently mounted, making the overall weight of the product smaller, and is used in cases where rotation or alignment is needed.
Patterns of Magnetization
Ring magnets may be magnetized in a variety of manners. The north and south poles are positioned on the flat surfaces in axial magnetization. The poles are circular in the case of radial magnetization. This is because they are flexible and can be used in various engineering requirements.
Materials
The vast majority of ring magnets are manufactured using neodymium (ndfeB), ceramic/ferrite, samarium cobalt (SmCo), or alnico. All materials influence the strength of the magnet, cost, and its ability to withstand environmental factors.
Magnetic Strength
Neodymium ring magnets are very strong; they are usually the strongest permanent magnets on the market. Even tiny ones have great loads. Even less powerful, ceramic ring magnets can also be used in cost-effective solutions.
Durability and Stability
Ring magnets can withstand high temperatures, resist corrosion, and be magnetically active, depending on the material used.
To sum up, ring magnets are one of the most convenient magnet designs in contemporary technology, due to the combination of hollow structure and strong materials.
Advantages of Ring Magnets

There are several advantages of ring magnets compared to other shapes and designs. We will examine their major strengths in more detail:
1. Strong Magnetic Force
Ring magnets, particularly magnets that are made of neodymium, possess very powerful magnetic fields. They can lift or support objects many times their own weight, although they are small. This is their strength and is applied in situations where precision and power are needed, such as electric generators or motors.
2. Compact design, high performance
The donut shape is not only aesthetic. It’s highly functional. Ring magnets can be easily incorporated into shafts, rods, and rotating machines through the central hole without causing unnecessary space. The small but high-energy design is essential in the current engineering of a high-performance system that should not occupy much space.
3. Durable
The selection of material determines the durability. Ceramic ring magnets do not corrode naturally, whereas the neodymium magnets are generally covered with nickel, zinc or epoxy to ensure that they do not rust. Samarium cobalt magnets are not only resistant to corrosion, but can withstand heat as well. This strength implies that the ring magnets will take years before they lose their magnetism.
4. Multi-Functional
Ring magnets are also the most versatile magnets. They are applicable in speakers, motors, renewable energy systems, medical devices, toys, and even do-it-yourself science projects. Their design allows them to also be useful in industrial machines as well as in common products.
How Do Ring Magnets Work?
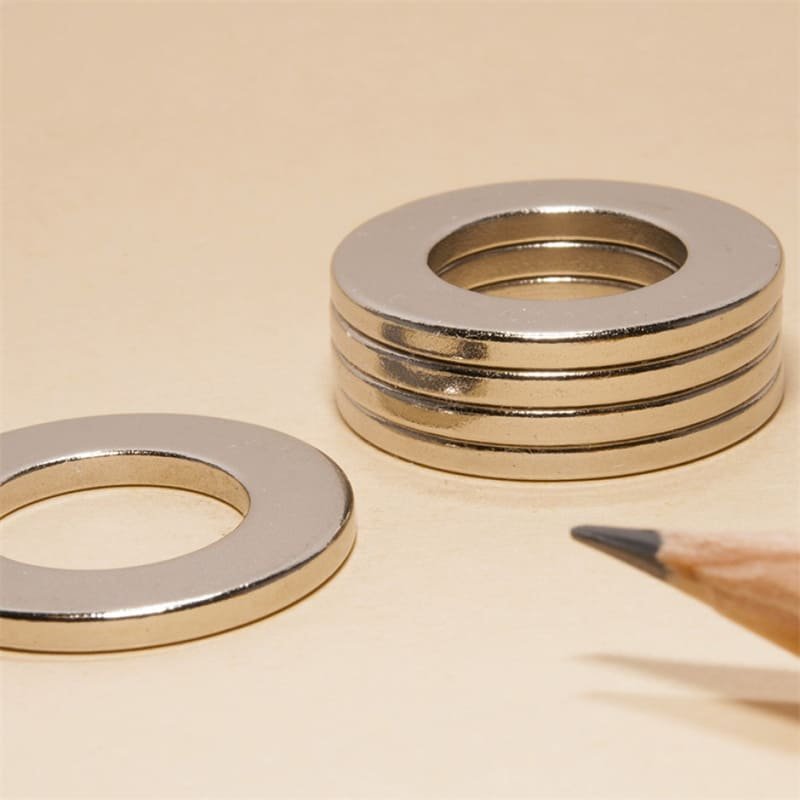

In order to get a sense of how the ring magnets operate, it is necessary to first find out how magnets operate. A magnet generates a magnetic field – an invisible energy that can pull some metals such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
The odd magnetic field is influenced by the unusual ring shape. In an axially magnetized ring, the north and south poles are on the flat circular faces, forming a tugging force perpendicular to the thickness of the ring. This is a type that is widespread in holding and lifting applications.
The poles in a radially magnetized ring are at the edges of the ring and form a circular magnetic field. This kind is particularly applicable in motors and rotary machines, where the circular shape of the magnet boosts the efficiency of movement.
The hollow core is also convenient; it can be used to send mechanical components (such as rods, screws, or shafts) through the middle without disturbing the magnetic field. This is the reason why moving or rotating systems can use the ring magnets.
Applications of Ring Magnets
Ring magnets are highly diverse and can be located in various sectors. We will look at some of the most significant applications:
1. Industrial Applications
Motors and Generators: Ring magnets play a vital role in the motors, where they assist in the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. They are also employed in wind turbines and generators in the production of electricity.
Sensors and Measuring Instruments
Speed sensors, torque sensors, and other measurement devices make use of ring magnets to obtain the right reading.
Loudspeakers
The loudspeakers: Loudspeakers are used by many speakers who use ring magnets to generate sound by vibrating the diaphragms in reaction to the changing electrical signals.
Medical Devices
MRI machines and other diagnostic devices use powerful ring magnets to make images and be very accurate.
2. DIY Projects
The industry is not the only place where ring magnets are used, as they are also widely used by hobbyists and makers. Some common DIY uses include:
• Constructing tailor-made motors or generators.
• Designing magnetic levitation apparatuses to experiment on.
• Their use as fasteners or carriers of small tools.
• Science experiment in the classroom to illustrate magnetism.
3. Renewable Energy Projects
Strong magnets are essential to renewable energy systems. Ring magnets are used significantly in:
Wind Turbines
These are used within generators to generate electricity more efficiently.
In EVs
Ring magnets are commonly used in the motors of EVs so that maximum power is obtained, and at the same time, the size of the motor remains small.
Solar Tracking Systems
In certain solar technologies, ring magnets are used to turn solar panels to allow the maximum amount of sunlight to reach the panel.
How to Choose the Right Ring Magnet?
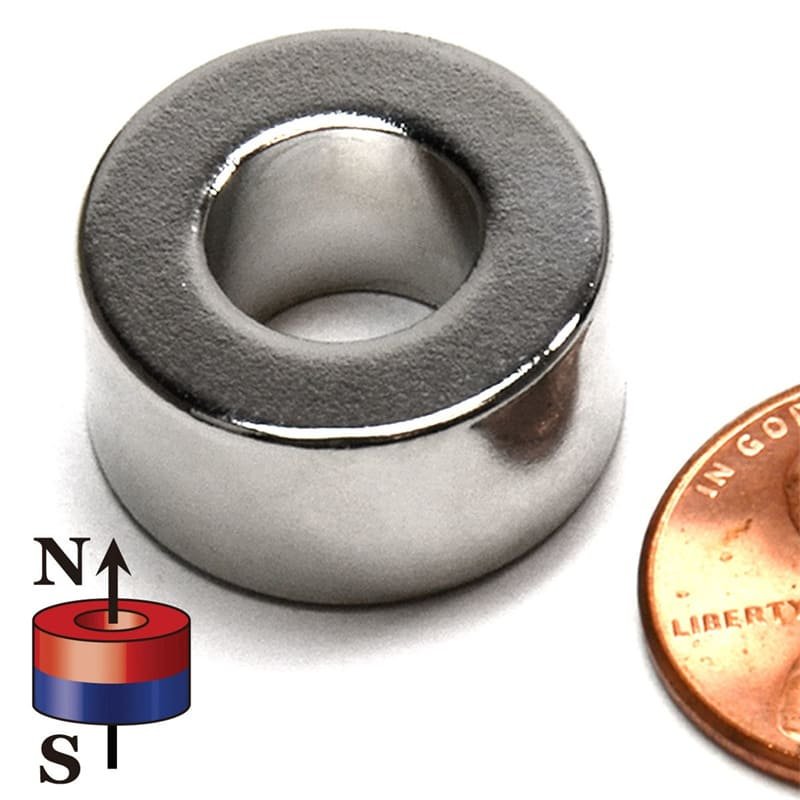

Not every ring magnet is made equal. It all depends on your project or industry to select the correct one. Here’s what to consider:
1. Magnet Material
Neodymium (NdFeB)
The strongest, however requires a protective coating. Most suitable when it needs to be fast and small.
Ceramic/Ferrite
Inexpensive, rust-resistant, and stronger, but less durable. Economical on the budget.
Samarium Cobalt (SmCo)
Hard and very heat and corrosion-resistant. Suited to high temperatures.
Alnico
Not as strong as neodymium or SmCo, but can be used at high temperatures.
2. Magnet Strength
You must know the necessary force needed to pull. In heavy work or industry, neodymium magnets are used. Ceramic magnets can be used in lighter applications.
3. Temperature Considerations
High temperature causes loss of strength in magnets. At temperatures above 80 °C, Neodymium is weak, and SmCo and Alnico are stronger at higher temperatures. Never select without first checking the temperature limits.
4. Magnet Size
The field strength is influenced by the size (outer diameter, inner diameter and thickness). A bigger magnet can produce more power, but might not be suitable in small devices. Select the size to suit your design.
5. Magnet Shape
Even in ring magnets, there are proportions. A fat ring will pull better than a thin one. Give thought to the trade-off involving size and magnetic power.
Final Thoughts
Ring magnets might look simple, but they are one of the strongest and useful magnet shapes on the market. Their hollow nature and strong properties of magnetism make them indispensable to modern technology.
Ring magnets have found their value in numerous applications, be it in motors and renewable energy, in medical devices, and in DIY work. The correct selection of one is based on factors such as material, strength, size, and operating temperature.
Technology does not stand still, and the need for especially small but powerful solutions will keep increasing, and the ring magnets will stay in the focus of most changes. You might be either an engineer, a student, or even a hobbyist, but knowing about ring magnets can open up new vistas in design and creativity.
FAQs
What is the difference between Neodymium Ring and Ceramic Ring Magnets?
Neodymium magnets are stronger but costly and have to have a coating to prevent rust. Ceramic magnets are also cheaper, weaker, and intrinsically corrosion-resistant.
What are ring magnets made of?
Most are typically neodymium, ceramic/ferrite, samarium cobalt, or alnico engineered magnetic materials.
Are ring magnets strong?
Yes. Even very small neodymium ring magnets are very powerful. Ceramic ones are not that strong, but all-purpose.
What are the common materials used for ring magnets?
The top four include neodymium, ceramic/ferrite, samarium cobalt, and alnico.
Ring vs. disc/square magnets: Which is stronger given the same volume?
When of the same material and size, they are alike in strength. But in rotational systems, ring magnets are the best, and discs or blocks are the best in flat contact surfaces.
What are the limitations of strong magnetic transportation/aviation?
Planes may have sensitive navigation equipment that these very large and strong magnets can interfere with. This is the reason strong neodymium magnets shipped by air must be specially packaged and safety-approved.

I’m Ben, with over 10 years in the permanent magnet industry. Since 2019, I’ve been with Osenc, specializing in custom NdFeB magnet shapes, magnetic accessories, and assemblies. Leveraging deep magnetic expertise and trusted factory resources, we offer one-stop solutions—from material selection and design to testing and production—streamlining communication, accelerating development, and ensuring quality while reducing costs through flexible resource integration.