Magnetic field simulation is basically your “test lab on a screen,” and for many projects it’s the fastest way to run a magnet simulation before you ever touch a physical prototype. In this guide, we’ll break down what it is, the minimum magnetism basics you need, and how magnetic field simulation software (and other magnetic simulation software) turns your inputs (shape, materials, currents, layouts) into field maps, numbers, and performance predictions you can actually use.
We’ll then walk through practical tools and workflows for magnetic field modelling, the real benefits for designers and buyers (better magnet selection, fewer prototypes, faster development), and the limits you must watch for—like input accuracy, modeling assumptions, computing time, and the expertise needed to avoid wrong conclusions. Finally, we’ll show how Osenc applies simulation to refine custom magnets and assemblies before manufacturing.
Magnetic Field Simulation
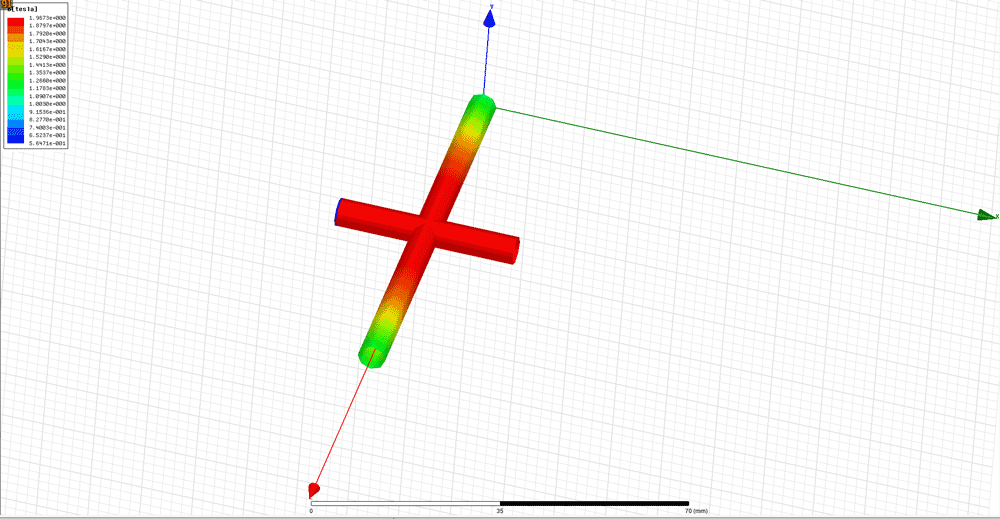
Magnetic field simulation is an important tool for magnet makers and users, especially when you need reliable magnetic field modeling to guide design decisions. This article will explore how magnetic field simulation works, how magnetic field simulation modeling is set up, and how it can help design and build better magnet systems.
1. Understanding Magnetic Field Simulation
A. Magnetism Basics
It’s hard to make sense of magnetic field simulation results—or do clean magnetic modeling / magnetic field modelling—without knowing some magnetism basics. For example, you might misunderstand the results if you don’t get how magnets work. Or you might set up the simulation wrong if you don’t know about the type of magnet you want to simulate.
1). Core Magnetism Ideas
If magnetism is new to you, learn some key laws and principles of how magnetic fields behave. These include things like magnetic poles, magnetic flux, and magnetic field strength. Also, how different magnetic fields interact. Understanding these basics is key to how magnetic field simulation works. It helps you get what the simulation is modeling and how it predicts how magnetic fields act.
2). Different Kinds of Magnets
There are many types of magnets, like permanent magnets (neodymium or ferrite), electromagnets, and induced magnets. Each acts in its own way.
Knowing how these magnet types differ, including their magnetic field strength, shape, and size, helps predict how they’ll act in different situations. The type of magnet you simulate has a big effect on the results. Understanding different magnet types means you can set up simulations better and figure out the results.
B. What is Magnetic Field Simulation?
Definition and Goal
Magnetic field simulation is a computer tool that figures out magnetic field patterns and details for a specific magnet system design—often grouped under magnet field simulation and broader electromagnetic field simulation workflows. It uses math techniques to solve Maxwell’s equations, which describe how electromagnetism works under certain conditions.
Simply put, you give details about your magnet system—size, shape, layouts, materials, currents, and boundary settings—then the solver uses those inputs to simulate magnetic field behavior in a controlled virtual environment. The software then virtually prototypes your design, breaking it into many small pieces (meshes), and calculates the magnetic field strength and direction everywhere.
Real-World Uses
Magnetic field simulation gives visual results (field lines or contour maps) and numerical outputs like magnetic flux density, peak field intensity, forces and inductance—so it can support magnetic flux simulation and magnetic force simulation for practical design checks. This lets you analyze how your magnet system may work and improve the design before building a physical prototype. This can optimize your product and cut down development time and cost.
Magnetic field simulation tools have gotten much more advanced in recent years, with many magnetic modelling software options (from beginner-friendly magnetism simulation tools to professional suites) across different complexity and price levels. They have become easy enough for any magnet designer or user to use for their projects. Simulation provides valuable insights into your magnetic system and predicts how it may act with high accuracy.
Importance for Magnet Users and Buyers
In short, magnetic field simulation calculates the magnetic field in and around your magnet system design based on what you input. It is a virtual prototyping tool that gives both visual and numerical results for thoroughly analyzing and optimizing your magnet system. The benefits of using magnetic field simulation are huge, especially reducing waste and speeding up development.
Why Simulate Magnetic Fields?
- I apply the Right-Hand Grip Rule to see how current direction changes magnetic poles, including simulating the field around a single wire carrying DC when I’m checking the basics.
- I experiment with multiple loops to watch how fields combine, and I use interactive simulations to make the patterns easier to understand.
- I visualize symmetry in both 2D and 3D, and I sometimes compare it to demos that displays the magnetic field of earth in 3D to build intuition.
- I explore how solenoids work in motors and transformers.
- I learn about MRI machines and other electromagnetic devices, where material behavior like ferromagnetic, paramagnetic, and diamagnetic responses can change real outcomes.
- I study the Biot-Savart law and its applications, and I connect it back to computational methods to predict the behavior of a magnetic fields in simulations.
- I experience phenomena similar to physical experiments, even when I cannot access lab equipment.
- I observe effects that are hard to see in a classroom, especially when the tool displays the magnetic field in a number of visual modes like field lines, contours, and slices.
🧲 Note: Simulations save me time and resources. I can test ideas before building anything, including changing the strength of forces in a magnetic field by adjusting gaps, materials, or magnet grades. This approach gives me confidence in my designs and helps me avoid costly mistakes.
In some learning demos, students move a virtual compass around a bar magnet to explore the interactions between a compass and bar magnet and describe the magnetic field around the magnet in plain language. It’s also a quick way to observe magnetic field lines for attracting and repelling magnets before you move on to more complex assemblies.
I rely on Osenc for expert advice when I need to simulate large or irregular-shaped magnets. Their experience in custom solutions makes my projects run smoothly.
2. Using Software for Magnetic Field Simulation
The ability to simulate and predict how magnetic fields act virtually is a huge leap forward. It has a big impact on many industries. But you don’t need to be an experienced engineer or magnetism expert to get the basics of these simulations. Here, we’ll look at some common software for magnetic field simulations, including options you might see labeled as magnet simulation software or magnetic field modeling software, and explain how these tools predict how magnets will act.
Autodesk Inventor
This software is widely used for 3D modeling, including making digital models of magnets and magnetic assemblies. With Autodesk Inventor, you can design and visualize your magnet or assembly in 3D before running magnetic field 3d simulation tasks (including full magnetic field simulation 3d post-processing views).
EMS
If you want an easy solution for magnetic field simulations, check out EMS. This user-friendly software lets you set up and run basic simulations. It gives you useful insights into how your magnetic field may act.
Maxwell
For detailed and precise simulations, Maxwell is a top choice. In many workflows it runs inside Ansys Electronics Desktop, where advanced solvers help improve accuracy for professional simulations.
Understanding How Simulations Predict Magnet Behavior
Magnetic field simulations depend on accurate calculations to predict how magnets will act. Correct modeling is key—when modeling magnetic fields, what you input directly impacts the results, so even small parameter mistakes can distort a simulation magnetic field outcome. Running a simulation lets you anticipate how a magnet may act under different conditions.
Factors Affecting How Magnets Perform
Different magnet types have properties that determine how they perform. For example, neodymium magnets act differently than ferrite magnets. Also, environment conditions like temperature and humidity can affect how magnets perform. Finally, boundary conditions, which define the space for the simulation, can significantly change the results.
Understanding these factors helps you make sense of simulation results and use them to decide which magnets to choose and how to use them.
Whether you’re a hobbyist, student, or just curious about the fascinating world of magnetism, understanding these simulations can open up lots of possibilities.
First Simulation Steps
Account Setup
Account Setup I always begin my magnetic field simulation journey by creating an account on the chosen platform. When I’m learning a new tool, I often follow a simple Worksheet for this simulation so I don’t miss setup details.Most platforms that offer magnetic field simulation online (often marketed as a magnet field simulator, magnetic field simulator, or even a lightweight magnet simulator) require a quick registration. I usually provide my email address, set a secure password, and verify my account through a confirmation link. This process takes less than five minutes.
Here’s my typical checklist for account setup:
- Visit the simulation platform’s website.
- Click the “Sign Up” or “Register” button.
- Enter my email and create a strong password.
- Confirm my email address through the link sent to my inbox.
- Log in and access the dashboard.
🛡️ Tip: I always use a unique password for each platform to keep my data safe.
Osenc’s engineering support team guided me through my first registration, making sure I had access to all the features needed for advanced simulations.
Select Simulation Type
Once I log in, I choose the type of simulation that matches my project goals. Most platforms offer several methods for analyzing magnetic fields, so you can choose the right approach for magnetic fields simulation depending on geometry, materials, and accuracy goals. I select the one that fits my needs best.
| Method | Solver Type | Discretization | Material Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDTD | Differential equation | Volumetric domain | Non-linear, anisotropic |
| FEM | Variational form | Volumetric domain | Non-linear, anisotropic, multi-physics |
| MoM/BEM | Integral equations | Surface currents | Linear, piecewise homogeneous |
I often use Finite Element Analysis (FEA) for accurate results in magnetic design. Sometimes, I try Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) or Method of Moments (MoM) for specific cases. Each method has strengths for different applications. For example, FEM works well for complex shapes and multi-physics problems, while MoM is great for surface current analysis.
📊 Note: I always read the platform’s documentation to understand which solver matches my project. Osenc’s experts helped me pick the right simulation type for my custom neodymium magnet assemblies.
Input Parameters
After selecting the simulation type, I enter the parameters that define my magnetic field simulation. Accurate input is essential for reliable results. I focus on the following key parameters:
| Essential Input Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Coil Type | Sets the coil’s behavior in the simulation |
| Topology | Shapes the magnetic field distribution |
| Number of Turns | Changes the field’s strength |
| Wire Diameter | Affects resistance and current flow |
| Material Properties | Determines how the magnet or coil responds |
| Geometry Dimensions | Sets the size and shape of the model |
I also describe my simulation goal clearly. For example, I might want to visualize the field lines around a 60-centimeter solenoid or calculate the field strength using the Biot–Savart Law. I sometimes add visuals to show the right-hand rule, which helps me understand the direction of the field.
🧑🔬 Pro Tip: I double-check every parameter before running the simulation. Even a small mistake, like entering the wrong number of turns, can change the results. Osenc’s team reviews my input when I work on complex or custom projects, ensuring I get precise outcomes every time.
Run Simulation
I always run my simulation by following a clear, step-by-step process. 🏁 This helps me avoid mistakes and ensures I get accurate results. Here is how I do it:
- Double-check all parameters: I review my coil type, number of turns, material properties, and geometry. Even a small error can change the outcome.
- Select the simulation mode: Most platforms offer options like “Quick Run” for fast results or “Detailed Analysis” for more data. I choose the mode that fits my project.
- Click the ‘Run’ or ‘Start Simulation’ button: I watch the progress bar or status indicator. Some simulations finish in seconds, while complex models may take several minutes.
- Monitor for errors or warnings: If the platform shows a message, I read it carefully. I fix any issues before continuing.
- Save my simulation session: I always save my work. This lets me review or share results later.
💡 Tip: I keep my browser open and avoid running other heavy programs. This keeps the simulation running smoothly.
Osenc’s engineering team once advised me to use the “Detailed Analysis” mode for a custom neodymium magnet project. Their guidance helped me spot a parameter error before I wasted time on a long run.
View Results
I view my simulation results using the platform’s visualization tools. 👀 This step helps me understand how the magnetic field behaves in my setup. Here is what I focus on:
- Field lines and strength: I look for clear field lines around magnets and coils, and I sometimes explore the interaction between Earth’s magnetic field and a bar magnet as a quick direction check. I check the color scale to see strong and weak areas.
- 3D and 2D views: I switch between 2D slices and 3D models, which is exactly what you want when reviewing magnetic field simulation 3d results and checking field distribution from multiple angles.
- Numeric data: I review tables showing field strength at specific points. For example, I might see a peak of 1.2 Tesla near the magnet’s surface.
- Export options: I save images or data files for reports or presentations.
3. Benefits of Magnetic Field Simulation
A. Predicting How Magnets Will Act
Figuring Out Magnetic Field Strength and Direction
A big benefit of magnetic field simulation is helping users and buyers understand a magnet’s field strength and direction without testing it physically. This is especially useful with big or pricey magnetic assemblies where physical testing takes time and costs a lot.
Predicting Performance in Different Conditions
Magnetic field simulations can also simulate different environments and how something is used. This allows users and buyers to predict how a magnet may perform under those conditions. This helps spot possible issues ahead of time and make sure the chosen magnet or magnetic assembly will work well for its intended purpose.
B. Helping Choose Magnets
Picking the Right Magnet for What You Need
By simulating how different magnet types may perform under various conditions, users and buyers can make better informed choices about which magnet best suits their needs. For example, a buyer could use a simulation to decide between neodymium and ferrite magnets for a specific use based on how they might perform under the simulated conditions.
Judging Quality and Value
Finally, magnetic field simulations can help users and buyers determine a magnet or magnetic assembly’s quality and value. For instance, a simulation may show a more expensive magnet performs a lot better than a cheaper one for the intended purpose, suggesting the pricier magnet is worth the extra cost. On the other hand, a simulation may show a cheaper magnet performs well enough for the intended purpose, indicating it offers better value.
In short, magnetic field simulations provide useful insights to guide users and buyers in choosing magnets. They help make better informed decisions and get the most for the money.
4. Limits of Magnetic Field Simulation
A. Accuracy Concerns
Shortcomings of Simulation Models
Magnetic field simulations rely on math models that simplify how things work in the real world. These models make assumptions to make the math and computing manageable. So, there can be times when the model fails to fully capture how something works in a real-world situation, leading to inaccuracies in the results.
How Accurate the Input Is Affects Accuracy
How accurate a simulation is depends a lot on how accurate the input is. If there are errors or uncertainties in what is input (such as properties of the magnet, conditions around it, or boundary conditions), these can carry through the simulation and affect the accuracy of the results.
B. Practical Considerations
Time and Computing Power Required
Simulations, especially those involving complex systems or needing to be very accurate, can require a lot of computing power and time. This can be a limit in cases where results are needed quickly or available computing resources are limited.
Need for Expertise to Run Simulations
While user-friendly software is available, running a magnetic field simulation and understanding the results often requires a certain level of expertise. Without this expertise, there is a risk of setting up the simulation incorrectly or misinterpreting the results, which can lead to inaccurate predictions and potentially costly mistakes.
So, while magnetic field simulations are a powerful tool, these limits must be kept in mind when using the results to make decisions.
Conclusion
Magnetic field simulation is an invaluable tool that offers numerous advantages for designers and users of magnet systems.
At Osenc, we utilize magnetic field simulation to deliver high-quality bespoke magnets and magnetic assemblies. Through simulation, we can refine your design, enhance performance, preempt issues, and curtail costs, all before the commencement of the manufacturing process.
While simulations have their limitations and cannot reproduce all real-world conditions, contemporary tools have grown considerably sophisticated, precise, and accessible. At Osenc, we employ simulation to acquire a comprehensive understanding of your magnet system’s behavior and performance. Through simulation, we can create superior custom solutions more swiftly and cost-effectively. We can identify and rectify issues early in the process when they are simpler to amend.
What sets Osenc apart from many magnet suppliers is our capability to conduct magnetic field simulation services for your custom designs. In essence, if you work with magnets or magnetic systems, you will derive substantial benefits from Osenc’s magnetic simulation capabilities. It empowers you to work more efficiently, make decisions with greater confidence, and construct solutions that may have seemed unattainable otherwise.
In conclusion, magnetic field simulation offers a multitude of benefits with substantial implications. While supplementing but not superseding physical prototyping, it provides a virtual prototyping environment where we can construct, test, analyze, optimize, and improve your magnet system designs to attain peak performance. By facilitating a faster, more economical and smarter design process, magnetic field simulation is a crucial tool that Osenc uses to provide the best custom magnet solutions for you.
With Osenc as your magnet ally and magnetic field simulation at our disposal, your products will attain unprecedented levels of performance and efficiency. Allow us to cater to your magnet requirements – we possess the capability to simulate, optimize, construct, and deliver high-quality custom magnetic assemblies for you.
FAQ
What information do I need before running a simulation?
I gather these details:
- Magnet size (e.g., 60 millimeters)
- Material type (like neodymium)
- Number of coil turns
- Current value
Accurate data gives me reliable results.
Can I simulate custom-shaped magnets?
Yes, I can. Many platforms let me draw or import custom shapes. For complex designs, I ask Osenc’s engineering team for help. 🛠️
How accurate are online magnetic field simulations?
Most online tools give results within 10% of real measurements for standard setups—however, magnetic field simulation software free or magnetfeld simulation freeware options may vary more, so always validate with measurements. (In German searches you may also see the term magnetfeldsimulation.) For high-precision needs, I use advanced settings or consult Osenc.

I’m Ben, with over 10 years in the permanent magnet industry. Since 2019, I’ve been with Osenc, specializing in custom NdFeB magnet shapes, magnetic accessories, and assemblies. Leveraging deep magnetic expertise and trusted factory resources, we offer one-stop solutions—from material selection and design to testing and production—streamlining communication, accelerating development, and ensuring quality while reducing costs through flexible resource integration.

